Purinergic modulation of cochlear partition resistance and its effect on the endocochlear potential in the Guinea pig
- PMID: 14976588
- PMCID: PMC2538371
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-003-4003-4
Purinergic modulation of cochlear partition resistance and its effect on the endocochlear potential in the Guinea pig
Abstract
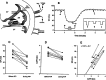
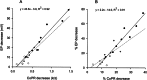
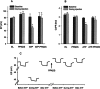
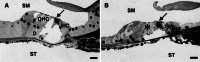
Introduction of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) into the endolymphatic compartment of the guinea-pig cochlea decreases the endocochlear potential (EP). To determine if this is due to an ATP-induced change in compartment resistance, the cochlear partition resistance (CoPR) was measured using constant current injections into scala media before, during, and after microinjection of ATP into the same compartment. The CoPR (mean = 3.13 +/- 0.13 kOmega) decreased with ATP in a dose-dependent manner (25.1 +/- 3.0% decrease in relation to baseline values) and this was linearly correlated ( R(2) = 0.91) to the magnitude of the ATP-induced decline in EP (41.6 +/- 7.0% decline in relation to the baseline). Pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid (PPADS, a P2X receptor antagonist) injected prior to ATP application blocked this ATP-induced reduction in EP and CoPR. This indicates that ATP-gated ion channels (P2X receptors) provide a latent shunt capable of regulating the majority of the electrical potential across the luminal surface of the sensory hair cells, which is necessary for sound transduction. The results suggest a novel sound transduction regulatory mechanism, which, via extracellular ATP, has the capability of adjusting hearing sensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P2X receptor-mediated changes in cochlear potentials arising from exogenous adenosine 5'-triphosphate in endolymph.Hear Res. 1999 Dec;138(1-2):56-64. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(99)00151-3. Hear Res. 1999. PMID: 10575114
-
Extracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) in the endolymphatic compartment influences cochlear function.Hear Res. 1995 Oct;90(1-2):106-118. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(95)00152-3. Hear Res. 1995. PMID: 8974987
-
Properties of ATP-gated ion channels assembled from P2X2 subunits in mouse cochlear Reissner's membrane epithelial cells.Purinergic Signal. 2015 Dec;11(4):551-60. doi: 10.1007/s11302-015-9473-4. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Purinergic Signal. 2015. PMID: 26424615 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signaling in the organ of Corti: Potential therapeutic targets of sensorineural hearing losses.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Sep;151:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.01.029. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30721767 Review.
-
[Potassium ion secretion and generation of the endocochlear potential in the stria vascularis].HNO. 1997 Apr;45(4):205-9. doi: 10.1007/s001060050105. HNO. 1997. PMID: 9221259 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Differential Effects of Hearing Loss Mutations in Homomeric P2X2 and Heteromeric P2X2/3 Receptors.Cells. 2025 Mar 29;14(7):510. doi: 10.3390/cells14070510. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214464 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between noise-induced sensorineural hearing loss and hypertension: pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic prospects.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Apr 7;19:1523149. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1523149. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40260077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent findings and emerging questions in cochlear noise injury.Hear Res. 2008 Nov;245(1-2):5-17. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2008.08.007. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Hear Res. 2008. PMID: 18790034 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Distribution of NTPDase5 and NTPDase6 and the regulation of P2Y receptor signalling in the rat cochlea.Purinergic Signal. 2010 Jun;6(2):249-61. doi: 10.1007/s11302-010-9190-y. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Purinergic Signal. 2010. PMID: 20806016 Free PMC article.
-
ATP activates P2X receptors to mediate gap junctional coupling in the cochlea.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Oct 5;426(4):528-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.119. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22982314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Housley GD. Extracellular nucleotide signaling in the inner ear. Mol. Neurobiol. 1998;16:21–48. - PubMed
-
- Housley GD, Greenwood D, Ashmore JF. Localization of cholinergic and purinergic receptors on outer hair cells isolated from the guinea-pig cochlea. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1992;249:265–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

