Accuracy of the volume and pressure displays of high frequency oscillators
- PMID: 14977906
- PMCID: PMC1756021
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2002.023937
Accuracy of the volume and pressure displays of high frequency oscillators
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effect of frequency on the accuracy of volume and pressure displays of high frequency oscillators.
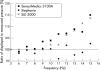
Methods: The effect of frequency on the displayed volume of the Stephanie, Dräger Babylog 8000 Plus, and SLE 5000 oscillators was assessed. A sine wave pump delivered a constant tidal volume at frequencies of 5-15 Hz to the patient manifold of the oscillators. The displayed volumes at each frequency were compared with the delivered volume. The effect of frequency on displayed pressure was assessed by connecting the oscillator's patient manifold to a lung model; three types of oscillator were studied (SensorMedics 3100A, SLE 5000, and Stephanie). Airway pressure was measured from the manifold using a pressure transducer and non-compliant tubing; the pressure measuring system had a flat frequency response to 30 Hz.
Results: The SLE 5000 volume display overread the delivered volume (by about 5%), but was not affected by frequency. At 5 Hz, the Dräger Babylog 8000 Plus and the Stephanie underread the delivered volume (by about 20%). Increasing frequency resulted in a greater discrepancy between the delivered and displayed volume with the Stephanie, but a smaller discrepancy with the Dräger Babylog 8000 Plus. Altering frequency had a small effect (maximum difference 6%) on the relation between the displayed and delivered pressure for all three oscillators.
Conclusion: Frequency affects the accuracy of displayed volumes and, to a lesser extent, displayed pressures of high frequency oscillators. The results emphasise that data displayed by new devices should not be uncritically accepted.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical