Role of NK cells and gamma interferon in transplacental passage of Toxoplasma gondii in a mouse model of primary infection
- PMID: 14977944
- PMCID: PMC356035
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1397-1401.2004
Role of NK cells and gamma interferon in transplacental passage of Toxoplasma gondii in a mouse model of primary infection
Abstract
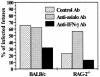
Protective immunity in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii is mainly mediated by NK cells, CD4 and CD8 T cells, and type 1 cytokines, such as gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). To clarify the roles of NK cells and IFN-gamma in protection against primary congenital toxoplasmosis, we used recombination activating gene 2 knockout (RAG-2(-/-)) mice, which lack T and B lymphocytes, in comparison with the wild-type BALB/c model. RAG-2(-/-) mice had a significantly lower risk of fetal toxoplasmosis than BALB/c mice (25 versus 63.9%; P = 0.003). This protection was associated with an increased number of maternal NK cells, IFN-gamma secretion by spleen cells, and decreased parasitemia. In the RAG-2(-/-) mice, NK cell depletion increased both the rate of fetal infection, to 56.5% (P = 0.02), and the blood parasite burden. Conversely, in the BALB/c mice, this treatment did not modify maternofetal transmission or the blood parasite burden. Neutralization of IFN-gamma in both infected RAG-2(-/-) and BALB/c mice decreased congenital Toxoplasma transmission, contrasting with an exacerbation of maternal infection. These data suggest that a partially protective immunity against congenital toxoplasmosis is achieved due to the increased number of NK cells in RAG-2(-/-) mice. However, it seems that IFN-gamma enhances, directly or indirectly, the transplacental transmission.
Figures



References
-
- Bancroft, G. J., R. D. Schreiber, G. C. Bosma, M. J. Bosma, and E. R. Unanue. 1987. A T cell-independent mechanism of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma. J. Immunol. 139:1104-1107. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann, V., S. D. Sharma, and J. S. Remington. 1986. Different regulation of the L3T4-T cell subset by B cells in different mouse strains bearing the H-2K haplotype. J. Immunol. 137:2291-2297. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H. L., R. Kamath, J. L. Pace, S. W. Russel, and J. S. Hunt. 1994. Expression of the interferon-gamma receptor gene in mouse placentas is related to stage of gestation and is restricted to specific subpopulations of trophoblast cells. Placenta 15:109-121. - PubMed
-
- Dannemann, B. R., V. A. Morris, F. G. Araujo, and J. S. Remington. 1989. Assessment of human natural killer and lymphokine-activated killer cell cytotoxicity against Toxoplasma gondii trophozoites and brain cysts. J. Immunol. 143:2684-2691. - PubMed
-
- Delassus, S., G. C. Coutinho, C. Saucier, S. Darche, and P. Kourilsky. 1994. Differential cytokine expression in maternal blood and placenta during murine gestation. J. Immunol. 152:2411-2420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

