Bordetella pertussis infection of primary human monocytes alters HLA-DR expression
- PMID: 14977950
- PMCID: PMC356037
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1450-1462.2004
Bordetella pertussis infection of primary human monocytes alters HLA-DR expression
Abstract
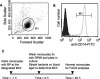
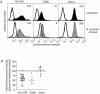
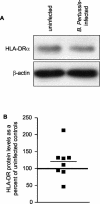
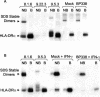
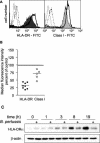
Bordetella pertussis is the causative agent of whooping cough, a potentially lethal respiratory disease in children. In immunocompetent individuals, B. pertussis infection elicits an effective adaptive immune response driven by activated CD4(+) T cells. However, live B. pertussis persists in the host for 3 to 4 weeks prior to clearance. Thus, B. pertussis appears to have evolved short-term mechanisms for immune system evasion. We investigated the effects of B. pertussis wild-type strain BP338 on antigen presentation in primary human monocytes. BP338 infection reduced cell surface expression of HLA-DR and CD86 but not that of major histocompatibility complex class I proteins. This change in cell surface HLA-DR expression reflected intracellular redistribution of HLA-DR. The proportion of peptide-loaded molecules was unchanged in infected cells, suggesting that intracellular retention occurred after peptide loading. Although B. pertussis infection of monocytes induced rapid and robust expression of interleukin-10 (IL-10), HLA-DR redistribution did not appear to be explained by increased IL-10 levels. BP338-infected monocytes exhibited reduced synthesis of HLA-DR dimers. Interestingly, those HLA-DR proteins that were generated appeared to be longer-lived than HLA-DR in uninfected monocytes. BP338 infection also prevented gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) induction of HLA-DR protein synthesis. Using mutant strains of B. pertussis, we found that reduction in HLA-DR surface expression was due in part to the presence of pertussis toxin whereas the inhibition of IFN-gamma induction of HLA-DR could not be linked to any of the virulence factors tested. These data demonstrate that B. pertussis utilizes several mechanisms to modulate HLA-DR expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of the class II MHC pathway in primary human monocytes by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 1;171(5):2374-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.5.2374. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12928384
-
Epstein-Barr virus encoded interleukin-10 inhibits HLA-class I, ICAM-1, and B7 expression on human monocytes: implications for immune evasion by EBV.Virology. 2002 Dec 20;304(2):342-51. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1716. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12504574
-
A natural pertactin deficient strain of Bordetella pertussis shows improved entry in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.New Microbiol. 2009 Apr;32(2):159-66. New Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19579693
-
Decreased inducible expression of CD80 and CD86 in human monocytes after ultraviolet-B irradiation: its involvement in inactivation of allogenecity.Blood. 1996 Mar 15;87(6):2386-93. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8630402
-
Impaired regulation of HLA-DR expression in human immunodeficiency virus-infected monocytes.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002 Jul;9(4):739-46. doi: 10.1128/cdli.9.4.739-746.2002. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12093667 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Reinvestigating the Coughing Rat Model of Pertussis To Understand Bordetella pertussis Pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2021 Nov 16;89(12):e0030421. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00304-21. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 34125597 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of newborn piglets with Bordetella pertussis: a new model for pertussis.Infect Immun. 2005 Jun;73(6):3636-45. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3636-3645.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15908393 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella Pertussis Toxin does not induce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human whole blood.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2012 Aug;201(3):327-35. doi: 10.1007/s00430-012-0238-1. Epub 2012 Apr 15. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22527330
-
Intracellular trafficking of Bordetella pertussis in human macrophages.Infect Immun. 2010 Mar;78(3):907-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01031-09. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20065021 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies SNPs in the MHC class II loci that are associated with self-reported history of whooping cough.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Oct 15;24(20):5930-9. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv293. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26231221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arunachalam, B., M. Pan, and P. Cresswell. 1998. Intracellular formation and cell surface expression of a complex of an intact lysosomal protein and MHC class II molecules. J. Immunol. 160:5797-5806. - PubMed
-
- Bakke, O., and T. W. Nordeng. 1999. Intracellular traffic to compartments for MHC class II peptide loading: signals for endosomal and polarized sorting. Immunol. Rev. 172:171-187. - PubMed
-
- Barcova, M., C. Speth, L. Kacani, F. Ubrall, H. Stoiber, and M. P. Dierich. 1999. Involvement of adenylate cyclase and p70S6-kinase activation in IL-10 up-regulation in human monocytes by gp41 envelope protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Pflueg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 437:538-546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

