Adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis synergizes with lipopolysaccharide to promote innate interleukin-10 production and enhances the induction of Th2 and regulatory T cells
- PMID: 14977963
- PMCID: PMC356053
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1568-1579.2004
Adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis synergizes with lipopolysaccharide to promote innate interleukin-10 production and enhances the induction of Th2 and regulatory T cells
Abstract
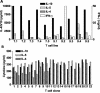
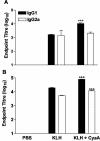
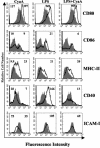
Adenylate cyclase toxin (CyaA) from Bordetella pertussis can subvert host immune responses allowing bacterial colonization. Here we have examined its adjuvant and immunomodulatory properties and the possible contribution of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), known to be present in purified CyaA preparations. CyaA enhanced antigen-specific interleukin-5 (IL-5) and IL-10 production and immunoglobulin G1 antibodies to coadministered antigen in vivo. Antigen-specific CD4(+)-T-cell clones generated from mice immunized with antigen and CyaA had cytokine profiles characteristic of Th2 or type 1 regulatory T (Tr1) cells. Since innate immune cells direct the induction of T-cell subtypes, we examined the influence of CyaA on activation of dendritic cells (DC) and macrophages. CyaA significantly augmented LPS-induced IL-6 and IL-10 and inhibited LPS-driven tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-12p70 production from bone marrow-derived DC and macrophages. CyaA also enhanced cell surface expression of CD80, CD86, and major histocompatibility class II on immature DC. The stimulatory activity of our CyaA preparation for IL-10 production and CD80, CD86, and major histocompatibility complex class II expression was attenuated following the addition of polymyxin B or with the use of DC from Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4-defective mice. However, treatment of DC with LPS alone at the concentration present in the CyaA preparation (0.2 ng/ml) failed to activate DC in vitro. Our findings demonstrate that activation of innate cells in vitro by CyaA is dependent on a second signal through a TLR and that CyaA can promote Th2/Tr1-cell responses by inhibiting IL-12 and promoting IL-10 production by DC and macrophages.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin modulates innate and adaptive immune responses: distinct roles for acylation and enzymatic activity in immunomodulation and cell death.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 15;175(2):730-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.2.730. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16002668
-
Toll-like receptor 4-mediated innate IL-10 activates antigen-specific regulatory T cells and confers resistance to Bordetella pertussis by inhibiting inflammatory pathology.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 15;171(6):3119-27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3119. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12960338
-
Adenylate cycalse toxin of Bordetella pertussis inhibits TLR-induced IRF-1 and IRF-8 activation and IL-12 production and enhances IL-10 through MAPK activation in dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Jul;84(1):234-43. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0208113. Epub 2008 Apr 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18401006
-
Effects of cholera toxin on innate and adaptive immunity and its application as an immunomodulatory agent.J Leukoc Biol. 2004 May;75(5):756-63. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1103534. Epub 2004 Jan 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. PMID: 14704372 Review.
-
The adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis--a novel promising vehicle for antigen delivery to dendritic cells.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Apr;293(7-8):571-6. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00291. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15149033 Review.
Cited by
-
Calpain-Mediated Processing of Adenylate Cyclase Toxin Generates a Cytosolic Soluble Catalytically Active N-Terminal Domain.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 26;8(6):e67648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067648. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840759 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-4 expression in infants with pertussis infection.Infection. 2013 Feb;41(1):195-8. doi: 10.1007/s15010-012-0288-8. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Infection. 2013. PMID: 22753132
-
Bioengineering of Bordetella pertussis Adenylate Cyclase Toxin for Antigen-Delivery and Immunotherapy.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jul 20;10(7):302. doi: 10.3390/toxins10070302. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30037010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific humoral immune response induced by propionibacterium acnes can prevent Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection in mice.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014 Mar;21(3):407-16. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00667-13. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24429068 Free PMC article.
-
Invasion of Dendritic Cells, Macrophages and Neutrophils by the Bordetella Adenylate Cyclase Toxin: A Subversive Move to Fool Host Immunity.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Sep 21;9(10):293. doi: 10.3390/toxins9100293. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28934122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akira, S. 2003. Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 278:38105-38108. - PubMed
-
- Bagley, K. C., S. F. Abdelwahab, R. G. Tuskan, T. R. Fouts, and G. K. Lewis. 2002. Pertussis toxin and the adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis activate human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and dominantly inhibit cytokine production through a cAMP-dependent pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 72:962-969. - PubMed
-
- Confer, D. L., and J. W. Eaton. 1982. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science 217:948-950. - PubMed
-
- Coote, J. G. 1992. Structural and functional relationships among the RTX toxin determinants of gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 8:137-161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

