Conservation and diversity of sap homologues and their organization among Campylobacter fetus isolates
- PMID: 14977980
- PMCID: PMC356032
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1715-1724.2004
Conservation and diversity of sap homologues and their organization among Campylobacter fetus isolates
Abstract
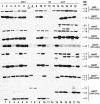
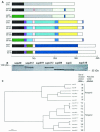
Campylobacter fetus surface layer proteins (SLPs), encoded by sapA homologues, are important in virulence. In wild-type C. fetus strain 23D, all eight sapA homologues are located in the 54-kb sap island, and SLP expression reflects the position of a unique sapA promoter in relation to the sapA homologues. The extensive homologies in the sap island include both direct and inverted repeats, which allow DNA rearrangements, deletion, or duplication; these elements confer substantial potential for genomic plasticity. To better understand C. fetus sap island diversity and variation mechanisms, we investigated the organization and distribution of sapA homologues among 18 C. fetus strains of different subspecies, serotypes, and origins. For all type A strains, the boundaries of the sap island were relatively consistent. A 187-bp noncoding DNA insertion near the upstream boundary of the sap island was found in two of three reptile strains studied. The sapA homologue profiles were strain specific, and six new sapA homologues were recognized. Several homologues from reptile strains are remarkably conserved in relation to their corresponding mammalian homologues. In total, the observed differences suggest that the sap island has evolved differing genotypes that are plastic, perhaps enabling colonization of varied niches, in addition to antigenic variation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structure and genotypic plasticity of the Campylobacter fetus sap locus.Mol Microbiol. 2003 May;48(3):685-98. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03463.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12694614 Free PMC article.
-
A deletion in the sapA homologue cluster is responsible for the loss of the S-layer in Campylobacter fetus strain TK.Arch Microbiol. 1997 Apr;167(4):196-201. doi: 10.1007/s002030050435. Arch Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9075619
-
Rearrangement of sapA homologs with conserved and variable regions in Campylobacter fetus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7265-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7265. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8346244 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter surface-layers (S-layers) and immune evasion.Ann Periodontol. 2002 Dec;7(1):43-53. doi: 10.1902/annals.2002.7.1.43. Ann Periodontol. 2002. PMID: 16013216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of Campylobacter fetus surface layer protein expression.Mol Microbiol. 1997 Nov;26(3):433-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.6151958.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9402015 Review.
Cited by
-
Campylobacter fetus of reptile origin as a human pathogen.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Sep;42(9):4405-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.9.4405-4407.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15365057 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic relationships among reptilian and mammalian Campylobacter fetus strains determined by multilocus sequence typing.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Mar;48(3):977-80. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01439-09. Epub 2010 Jan 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20053851 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic divergence of Campylobacter fetus strains of mammal and reptile origins.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jul;43(7):3334-40. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.7.3334-3340.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16000457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg, R. L., J. W. Jutila, and B. D. Firehammer. 1971. A revised classification of Vibrio fetus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 32:11-22. - PubMed
-
- Blaser, M. J., P. F. Smith, J. A. Hopkins, I. Heinzer, J. H. Bryner, and W. L. Wang. 1987. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections: serum resistance associated with high-molecular-weight surface proteins. J. Infect. Dis. 155:696-706. - PubMed
-
- Blaser, M. J., and Z. Pei. 1993. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections: critical role of high-molecular-weight S-layer proteins in virulence. J. Infect. Dis. 167:372-377. - PubMed
-
- Blaser, M. J., E. Wang, M. K. Tummuru, R. Washburn, S. Fujimoto, and A. Labigne. 1994. High-frequency S-layer protein variation in Campylobacter fetus revealed by sapA mutagenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 14:453-462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

