P2Y purinergic receptor regulation of CFTR chloride channels in mouse cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 14978203
- PMCID: PMC1664988
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.059881
P2Y purinergic receptor regulation of CFTR chloride channels in mouse cardiac myocytes
Abstract
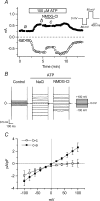
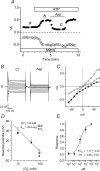
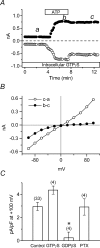
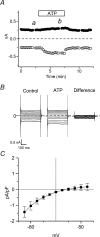
The intracellular signalling pathways and molecular mechanisms responsible for P2-purinoceptor-mediated chloride (Cl(-)) currents (I(Cl,ATP)) were studied in mouse ventricular myocytes. In standard NaCl-containing extracellular solutions, extracellular ATP (100 microm) activated two different currents, I(Cl,ATP) with a linear I-V relationship in symmetrical Cl(-) solutions, and an inwardly rectifying cation conductance (cationic I(ATP)). Cationic I(ATP) was selectively inhibited by Gd(3+) and Zn(2+), or by replacement of extracellular NaCl by NMDG; I(Cl,ATP) was Cl(-) selective, and inhibited by replacement of extracellular Cl(-) by Asp(-); both currents were prevented by suramin or DIDS pretreatment. In GTPgammaS-loaded cells, I(Cl,ATP) was irreversibly activated by ATP, but cationic I(ATP) was still regulated reversibly. GDPbetaS prevented activation of the I(Cl,ATP,) even though pertussis toxin pretreatment did not modulate I(Cl,ATP). These results suggest that activation of I(Cl,ATP) occurs via a G-protein coupled P2Y purinergic receptor. The I(Cl,ATP) persistently activated by GTPgammaS, was inhibited by glibenclamide but not by DIDS, thus exhibiting known pharmacological properties of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) Cl(-) channels. In ventricular cells of cftr(-/-) mice, extracellular ATP activated cationic I(ATP), but failed to activate any detectable I(Cl,ATP). These results provide compelling evidence that activation of CFTR Cl(-) channels in mouse heart are coupled to G-protein coupled P2Y purinergic receptors.
Figures

References
-
- Devuyst O, Guggino WB. Chloride channels in the kidney: lessons learned from knockout animals. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002;283:F1176–F1191. - PubMed
-
- Dubyak GR. Knock-out mice reveal tissue-specific roles of P2Y receptor subtypes in different epithelia. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:773–776. - PubMed
-
- Ehara T, Ishihara K. Anion channels activated by adrenaline in cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1990;347:284–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

