Basolateral anion transport mechanisms underlying fluid secretion by mouse, rat and guinea-pig pancreatic ducts
- PMID: 14978209
- PMCID: PMC1664956
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.061762
Basolateral anion transport mechanisms underlying fluid secretion by mouse, rat and guinea-pig pancreatic ducts
Abstract
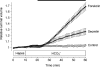
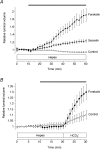
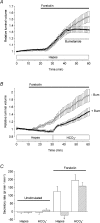
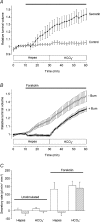
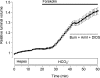
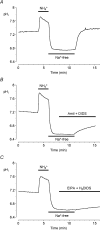
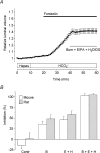
Fluid secretion by interlobular pancreatic ducts was determined by using video microscopy to measure the rate of swelling of isolated duct segments that had sealed following overnight culture. The aim was to compare the HCO(3)(-) requirement for secretin-evoked secretion in mouse, rat and guinea-pig pancreas. In mouse and rat ducts, fluid secretion could be evoked by 10 nm secretin and 5 microm forskolin in the absence of extracellular HCO(3)(-). In guinea-pig ducts, however, fluid secretion was totally dependent on HCO(3)(-). Forskolin-stimulated fluid secretion by mouse and rat ducts in the absence of HCO(3)(-) was dependent on extracellular Cl(-) and was completely inhibited by bumetanide (30 microm). It was therefore probably mediated by a basolateral Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransporter. In the presence of HCO(3)(-), forskolin-stimulated fluid secretion was reduced approximately 40% by bumetanide, approximately 50% by inhibitors of basolateral HCO(3)(-) uptake (3 microm EIPA and 500 microm H(2)DIDS), and was totally abolished by simultaneous application of all three inhibitors. We conclude that the driving force for secretin-evoked fluid secretion by mouse and rat ducts is provided by parallel basolateral mechanisms: Na(+)-H(+) exchange and Na(+)-HCO(3)(-) cotransport mediating HCO(3)(-) uptake, and Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransport mediating Cl(-) uptake. The absence or inactivity of the Cl(-) uptake pathway in the guinea-pig pancreatic ducts may help to account for the much higher concentrations of HCO(3)(-) secreted in this species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cl(-)-dependent secretory mechanisms in isolated rat bile duct epithelial units.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001 Aug;281(2):G438-46. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2001.281.2.G438. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11447024
-
5-hydroxytryptamine strongly inhibits fluid secretion in guinea pig pancreatic duct cells.J Clin Invest. 2001 Sep;108(5):749-56. doi: 10.1172/JCI12312. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11544281 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid secretion in interlobular ducts isolated from guinea-pig pancreas.J Physiol. 1998 Sep 1;511 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):407-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.407bh.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9706019 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Slc26a6 deletion and CFTR inhibition on HCO3- secretion by mouse pancreatic duct.J Med Invest. 2009;56 Suppl:332-5. doi: 10.2152/jmi.56.332. J Med Invest. 2009. PMID: 20224218 Review.
-
Apical Cl-/HCO3- exchanger stoichiometry in the modeling of HCO3- transport by pancreatic duct epithelium.J Med Invest. 2009;56 Suppl:325-8. doi: 10.2152/jmi.56.325. J Med Invest. 2009. PMID: 20224216 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic bicarbonate secretion involves two proton pumps.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):280-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136382. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20978133 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insight Into the Role of CFTR in Lacrimal Gland Duct Function in Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Jan 1;59(1):54-62. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22533. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29305607 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Na+-K+-2Cl- Cotransporter Activity in Rabbit Lacrimal Gland Duct Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Jul 1;57(8):3828-35. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18462. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27438543 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic duct secretion: experimental methods, ion transport mechanisms and regulation.J Physiol Biochem. 2008 Sep;64(3):243-57. doi: 10.1007/BF03178846. J Physiol Biochem. 2008. PMID: 19244938 Review.
-
IRBIT governs epithelial secretion in mice by antagonizing the WNK/SPAK kinase pathway.J Clin Invest. 2011 Mar;121(3):956-65. doi: 10.1172/JCI43475. Epub 2011 Feb 7. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21317537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Argent BE, Arkle S, Cullen MJ, Green R. Morphological, biochemical and secretory studies on rat pancreatic ducts maintained in tissue culture. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986;71:633–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

