Amyloid beta peptide load is correlated with increased beta-secretase activity in sporadic Alzheimer's disease patients
- PMID: 14978286
- PMCID: PMC373514
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0205689101
Amyloid beta peptide load is correlated with increased beta-secretase activity in sporadic Alzheimer's disease patients
Abstract
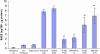
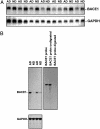
Whether elevated beta-secretase (BACE) activity is related to plaque formation or amyloid beta peptide (Abeta) production in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains remains inconclusive. Here, we report that we used sandwich enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay to quantitate various Abeta species in the frontal cortex of AD brains homogenized in 70% formic acid. We found that most of the Abeta species detected in rapidly autopsied brains (<3 h) with sporadic AD were Abeta(1-x) and Abeta(1-42), as well as Abeta(x-42). To establish a linkage between Abeta levels and BACE, we examined BACE protein, mRNA expression and enzymatic activity in the same brain region of AD brains. We found that both BACE mRNA and protein expression is elevated in vivo in the frontal cortex. The elevation of BACE enzymatic activity in AD is correlated with brain Abeta(1-x) and Abeta(1-42) production. To examine whether BACE elevation was due to mutations in the BACE-coding region, we sequenced the entire ORF region of the BACE gene in these same AD and nondemented patients and performed allelic association analysis. We found no mutations in the ORF of the BACE gene. Moreover, we found few changes of BACE protein and mRNA levels in Swedish mutated amyloid precursor protein-transfected cells. These findings demonstrate correlation between Abeta loads and BACE elevation and also suggest that as a consequence, BACE elevation may lead to increased Abeta production and enhanced deposition of amyloid plaques in sporadic AD patients.
Figures




References
-
- Selkoe, D. J. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81, 741-766. - PubMed
-
- Younkin, S. G. (1998) J. Physiol. (Paris) 92, 289-292. - PubMed
-
- Glenner, G. G. & Wong, C. W. (1984) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 120, 885-890. - PubMed
-
- Mullan, M., Crawford, F., Axelman, K., Houlden, H., Lilius, L., Winblad, B. & Lannfelt, L. (1992) Nat. Genet. 1, 345-347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

