Structure of the archaeal translation initiation factor aIF2 beta from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: implications for translation initiation
- PMID: 14978306
- PMCID: PMC2286745
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.03506604
Structure of the archaeal translation initiation factor aIF2 beta from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: implications for translation initiation
Abstract
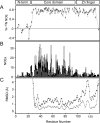
aIF2 beta is the archaeal homolog of eIF2 beta, a member of the eIF2 heterotrimeric complex, implicated in the delivery of Met-tRNA(i)(Met) to the 40S ribosomal subunit. We have determined the solution structure of the intact beta-subunit of aIF2 from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. aIF2 beta is composed of an unfolded N terminus, a mixed alpha/beta core domain and a C-terminal zinc finger. NMR data shows the two folded domains display restricted mobility with respect to each other. Analysis of the aIF2 gamma structure docked to tRNA allowed the identification of a putative binding site for the beta-subunit in the ternary translation complex. Based on structural similarity and biochemical data, a role for the different secondary structure elements is suggested.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure of the ternary initiation complex aIF2-GDPNP-methionylated initiator tRNA.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Mar 25;19(4):450-4. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2259. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22447243
-
Crystal structure of the intact archaeal translation initiation factor 2 demonstrates very high conformational flexibility in the alpha- and beta-subunits.J Mol Biol. 2008 Oct 10;382(3):680-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.07.039. Epub 2008 Jul 22. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18675278
-
Structure of an archaeal heterotrimeric initiation factor 2 reveals a nucleotide state between the GTP and the GDP states.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Nov 20;104(47):18445-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706784104. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18000047 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic free energies in translational GTPases: Classic allostery and the rest.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1850(5):1006-1016. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.07.006. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25047891 Review.
-
Translation initiation in Archaea: conserved and domain-specific features.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Jan;39(1):89-93. doi: 10.1042/BST0390089. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21265752 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Plasmodium falciparum Translation Initiation eIF2β Subunit: Direct Interaction with Protein Phosphatase Type 1.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 26;7:777. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00777. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27303372 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular view of 43 S complex formation and start site selection in eukaryotic translation initiation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 9;285(28):21203-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R110.119743. Epub 2010 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20444698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional anthology of intrinsic disorder. 3. Ligands, post-translational modifications, and diseases associated with intrinsically disordered proteins.J Proteome Res. 2007 May;6(5):1917-32. doi: 10.1021/pr060394e. Epub 2007 Mar 29. J Proteome Res. 2007. PMID: 17391016 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal domain of the human eIF2beta subunit and the CK2 phosphorylation sites are required for its function.Biochem J. 2006 Feb 15;394(Pt 1):227-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050605. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16225457 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of archaeal translational initiation factor 2 betagamma-GDP reveals significant conformational change of the beta-subunit and switch 1 region.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 29;103(35):13016-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604165103. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16924118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asano, K., Krishnamoorthy, T., Phan, L., Pavitt, G.D., and Hinnebusch, A.G. 1999. Conserved bipartite motifs in yeast eIF5 and eIF2B epsilon, GTPase-activating and GDP-GTP exchange factors in translation initiation, mediate binding to their common substrate eIF2. EMBO J. 18 1673–1688. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartels, C., Xia, T., Billeter, M., Güntert, P., and Wüthrich, K. 1995. The program XEASY for computer-supported NMR spectral analysis of biological macromolecules. J. Biomol. NMR 6 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Batchelor, H.A., Piper, D.E., de la Brousse, F.C., McKnight, S.L., and Wolberger, C. 1998. The structure of GABPα/β: An ETS domain-ankyrin repeat heterodimer bound to DNA. Science 279 1037–1041. - PubMed
-
- Bax, A. and Grzesiek, S. 1993. Methodological advances in protein NMR. Acc. Chem. Res. 26 131–138.
-
- Bell, S.D. and Jackson, S.P. 1998. Transcription and translation in Archaea: A mosaic of eukaryal and bacterial features. Trends Microbiol. 6 222–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

