Intratumoural mRNA expression of genes from the oestradiol metabolic pathway and clinical and histopathological parameters of breast cancer
- PMID: 14979917
- PMCID: PMC400649
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr746
Intratumoural mRNA expression of genes from the oestradiol metabolic pathway and clinical and histopathological parameters of breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: The expression of the oestrogen receptor (ER) is one of the more important clinical parameters of breast cancer. However, the relationship between the ER and its ligand, oestradiol, and the enzymes that synthesise it are not well understood. The expression of mRNA transcripts of members of the oestradiol metabolic and signalling pathways including the ER was studied in detail.
Method: mRNA transcripts for aromatase (CYP19), 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase I, 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase II, ERalpha, ERbeta, steroid sulfatase (STS), oestradiol sulfotransferase (EST), cyclin D1 (CYCLD1) and ERBB2 were fluorometrically quantified by competitive RT-PCR using an internal standard in 155 breast carcinomas. In addition, the transcripts of CYP19 were analysed for alternative splicing/usage of exon 1 and an alternative poly A tail.
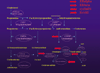
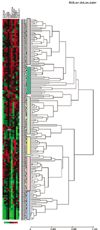
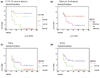
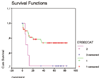
Results: A great variability of expression was observed, ranging from 0 to 2376 amol/mg RNA. The highest levels were observed for STS and EST, and the lowest levels (close to zero) were observed for the 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoenzymes. The levels of mRNA expression were analysed with respect to clinical and histopathological parameters as well as for disease-free survival. High correlation of the mRNA expression of STS, EST and 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the tumours suggested a common regulation, possibly by their common metabolite (oestradiol). Hierarchical clustering analysis in the 155 patients resulted in two main clusters, representing the ERalpha-negative and ERalpha-positive breast cancer cases. The mRNA expression of the oestradiol metabolising enzymes did not follow the expression of the ERalpha in all cases, leading to the formation of several subclasses of tumours. Patients with no expression of CYP19 and patients with high levels of expression of STS had significantly shorter disease-free survival time (P > 0.0005 and P < 0.03, respectively). Expression of ERbeta mRNA was a better prognostic factor than that of ERalpha in this material.
Conclusion: Our results indicate the importance of CYP19 and the enzymes regulating the oestrone sulfate metabolism as factors of disease-free survival in breast cancer, in addition to the well-known factors ER and ERBB2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of aromatase and 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 mRNA expression in predicting the clinical outcome of human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Sep;99(2):155-62. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9198-8. Epub 2006 Mar 16. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006. PMID: 16541304
-
Use of alternative promoters to express the aromatase cytochrome P450 (CYP19) gene in breast adipose tissues of cancer-free and breast cancer patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Nov;81(11):3843-9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.11.8923826. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996. PMID: 8923826
-
The relationship between the insulin-like growth factor-1 system and the oestrogen metabolising enzymes in breast cancer tissue and its adjacent non-cancerous tissue.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Oct;99(3):275-88. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9215-y. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006. PMID: 16752221
-
Recent insight on the control of enzymes involved in estrogen formation and transformation in human breast cancer.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Feb;93(2-5):221-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.02.007. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15860265 Review.
-
New developments in intracrinology of human breast cancer: estrogen sulfatase and sulfotransferase.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Feb;1155:76-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03683.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19250194 Review.
Cited by
-
The in vitro effects of 2-methoxyestradiol-bis-sulphamate on cell numbers, membrane integrity and cell morphology, and the possible induction of apoptosis and autophagy in a non-tumorigenic breast epithelial cell line.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2010 Dec;15(4):564-81. doi: 10.2478/s11658-010-0030-4. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20697831 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of CYP19A1 gene expression levels in women with breast cancer: a systematic review of the literature.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 Jun 14;76:e2846. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2846. eCollection 2021. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 34133482 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of the nonsteroidal steroid sulphatase inhibitor 667 COUMATE and its sequestration into red blood cells in rats.Br J Cancer. 2004 Oct 4;91(7):1399-404. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602130. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15328524 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Aromatase (CYP19A1) Expression Is Associated with a Poor Survival of Patients with Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer.Horm Cancer. 2018 Apr;9(2):128-138. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0317-2. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Horm Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29363090 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative use of multiple exons 1 of aromatase gene in cancerous and normal breast tissues from women over the age of 80 years.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(4):R48. doi: 10.1186/bcr2335. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19589174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lonning P, Borresen-Dale AL. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ, Witteveen AT, Schreiber GJ, Kerkhoven RM, Roberts C, Linsley PS, Bernards R, Friend SH. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002;415:530–536. doi: 10.1038/415530a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Utsumi T, Yoshimura N, Takeuchi S, Ando J, Maruta M, Maeda K, Harada N. Steroid sulfatase expression is an independent predictor of recurrence in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1999;59:377–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

