Alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes involved in vasoconstrictor responses to exogenous and neurally released noradrenaline in rat femoral resistance arteries
- PMID: 14980979
- PMCID: PMC1574265
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705690
Alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes involved in vasoconstrictor responses to exogenous and neurally released noradrenaline in rat femoral resistance arteries
Abstract
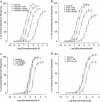
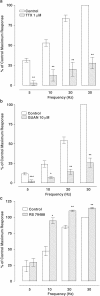
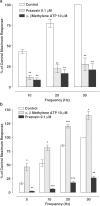
1. The alpha(1)-adrenoceptor subtypes involved in responses to exogenous and neurally released noradrenaline in rat femoral resistance arteries were characterised using a small vessel myograph, with antagonists prazosin (nonsubtype selective), 5-methyl-urapidil (alpha(1A)-selective), BMY 7378 (alpha(1D)-selective) and the alkylating agent chloroethylclonidine (preferential for alpha(1B)-). 2. Prazosin and 5-methyl-urapidil produced rightward shifts of the exogenous noradrenaline concentration - response curve (CRC) with pA(2) values of 9.2 and 9.1 respectively, in agreement with the presence of alpha(1A)-adrenoceptors. BMY 7378 (1 microm) shifted the noradrenaline CRC with an apparent pK(B) of 6.7, in agreement with the presence of alpha(1A)-, but not alpha(1D)-, adrenoceptors. Chloroethylclonidine at 1 microm had no effect and at 10 microm produced only a small reduction (c. 20%) in the maximum response to noradrenaline, indicating little, if any, contribution from alpha(1B)-adrenoceptors. 3. Responses of the rat femoral resistance arteries to electrical field stimulation (EFS) at 5-30 Hz for 10 s and 0.05 ms pulse width were principally due to alpha(1)-adrenoceptor stimulation. Prazosin and 5-methyl-urapidil inhibited EFS-mediated responses with pIC(50)s of 9.3 and 8.2, respectively, consistent with the alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor being the predominant subtype. Responses to EFS at 10-30 Hz were relatively insensitive to BMY 7378 (pIC(50), 6.5-6.7), while responses to 5 Hz were inhibited with a significantly higher pIC(50) of 8.02, suggesting the contribution of alpha(1D)-adrenoceptors. Chloroethylclonidine had no effect on responses to EFS, ruling out the contribution of an alpha(1B)-subtype. In the presence of cocaine, the predominant subtype involved in responses to EFS was the alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor, with a contribution from alpha(1D)-adrenoceptors at low frequency, as seen in the absence of cocaine. However, there was also a significant increase in the sensitivity to BMY 7378 at higher frequencies, suggesting that a further small alpha(1D)-adrenoceptor component may be uncovered in the presence of cocaine. 5. The present study has shown a predominant role of the alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor in contractions due to exogenous noradrenaline and to neurally released noradrenaline in rat femoral resistance arteries. alpha(1D)-Adrenoceptors are not involved in responses to exogenous noradrenaline but appear to be activated by neurally released noradrenaline at a low frequency of stimulation and at higher frequencies in the presence of neuronal-uptake blockade.
Figures


References
-
- ARGYLE S.A., McGRATH J.C. An α1A/α1L-adrenoceptor mediates contraction of canine subcutaneous resistance arteries. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000;295:627–633. - PubMed
-
- BLUE D.R., JR, BONHAUS D.W., FORD A.P.D.W., PFISTER J.R., SHARIF N.A., SHIEH I.A., VIMONT R.L., WILLIAMS T.J., CLARKE D.E. Functional evidence equating the pharmacologically-defined α1A- and cloned α1C-adrenoceptor: studies in the isolated perfused kidney of rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995;115:283–294. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BYLUND D.B., BOND R.A., CLARKE D.E., EIKENBURG J.P., HIEBLE J.P., LANGER S.Z., LEFKOWITZ R.J., MINNEMAN K.P., MOLINOFF P.B., RUFFOLO R.R., STROSBERG A.D., TRENDELENBURG U.G. Adrenoceptors, IUPHAR Receptor Compendium: London. 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

