Mammalian PAR-1 determines epithelial lumen polarity by organizing the microtubule cytoskeleton
- PMID: 14981097
- PMCID: PMC2172160
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200308104
Mammalian PAR-1 determines epithelial lumen polarity by organizing the microtubule cytoskeleton
Abstract
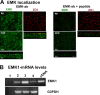
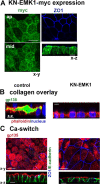
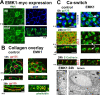
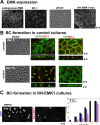
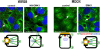
Epithelial differentiation involves the generation of luminal surfaces and of a noncentrosomal microtubule (MT) network aligned along the polarity axis. Columnar epithelia (e.g., kidney, intestine, and Madin-Darby canine kidney [MDCK] cells) generate apical lumina and orient MT vertically, whereas liver epithelial cells (hepatocytes and WIFB9 cells) generate lumina at cell-cell contact sites (bile canaliculi) and orient MTs horizontally. We report that knockdown or inhibition of the mammalian orthologue of Caenorhabditis elegans Par-1 (EMK1 and MARK2) during polarization of cultured MDCK and WIFB9 cells prevented development of their characteristic lumen and nonradial MT networks. Conversely, EMK1 overexpression induced the appearance of intercellular lumina and horizontal MT arrays in MDCK cells, making EMK1 the first known candidate to regulate the developmental branching decision between hepatic and columnar epithelial cells. Our experiments suggest that EMK1 primarily promotes reorganization of the MT network, consistent with the MT-regulating role of this gene product in other systems, which in turn controls lumen formation and position.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The novel PAR-1-binding protein MTCL1 has crucial roles in organizing microtubules in polarizing epithelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 15;126(Pt 20):4671-83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.127845. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23902687
-
Par-1 promotes a hepatic mode of apical protein trafficking in MDCK cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 21;101(38):13792-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403684101. Epub 2004 Sep 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15365179 Free PMC article.
-
Par1b promotes hepatic-type lumen polarity in Madin Darby canine kidney cells via myosin II- and E-cadherin-dependent signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Jun;18(6):2203-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0095. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17409351 Free PMC article.
-
Apical surface formation in MDCK cells: regulation by the serine/threonine kinase EMK1.Methods. 2003 Jul;30(3):269-76. doi: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00033-1. Methods. 2003. PMID: 12798141 Review.
-
Gastrulation: PARtaking of the bottle.Curr Biol. 2003 Mar 18;13(6):R223-5. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00155-6. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12646146 Review.
Cited by
-
Basolateral EGF receptor sorting regulated by functionally distinct mechanisms in renal epithelial cells.Traffic. 2013 Mar;14(3):337-54. doi: 10.1111/tra.12032. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 23205726 Free PMC article.
-
A protein interaction map for cell-cell adhesion regulators identifies DUSP23 as a novel phosphatase for β-catenin.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 3;6:27114. doi: 10.1038/srep27114. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27255161 Free PMC article.
-
KIF17 stabilizes microtubules and contributes to epithelial morphogenesis by acting at MT plus ends with EB1 and APC.J Cell Biol. 2010 Aug 9;190(3):443-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201006044. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20696710 Free PMC article.
-
Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus transformation in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell three-dimensional culture.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5379-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02323-09. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20219922 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF41 by the kinase Par-1b is required for epithelial cell polarity.J Cell Sci. 2014 Jan 15;127(Pt 2):315-27. doi: 10.1242/jcs.129148. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24259665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balczon, R., C.E. Varden, and T.A. Schroer. 1999. Role for microtubules in centrosome doubling in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. 42:60–72. - PubMed
-
- Bessone, S., F. Vidal, Y. Le Bouc, J. Epelbaum, M.T. Bluet-Pajot, and M. Darmon. 1999. EMK protein kinase-null mice: dwarfism and hypofertility associated with alterations in the somatotrope and prolactin pathways. Dev. Biol. 214:87–101. - PubMed

