Evaluation of acute hematologic and long-term pulmonary toxicities of radioimmunotherapy of Cryptococcus neoformans infection in murine models
- PMID: 14982795
- PMCID: PMC353163
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.3.1004-1006.2004
Evaluation of acute hematologic and long-term pulmonary toxicities of radioimmunotherapy of Cryptococcus neoformans infection in murine models
Abstract
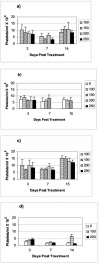
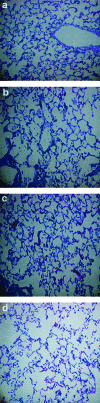
We evaluated acute hematological and long-term pulmonary toxicity of radioimmunotherapy in murine models of Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Activities up to 250 microCi were well tolerated by healthy A/JCr mice for (213)Bi-18B7 and (188)Re-18B7 monoclonal antibodies. In infected mice, doses up to 150 microCi produced only transient toxicity. The lungs of treated mice had no evidence of radiation fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Behr, T. M., M. Behe, M. G. Stabin, E. Wehrmann, C. Apostolidis, R. Molinet, F. Strutz, A. Fayyazi, E. Wieland, S. Gratz, L. Koch, D. M. Goldenberg, and W. Becker. 1999. High-linear energy transfer (LET) alpha versus low-LET beta emitters in radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors: therapeutic efficacy and dose-limiting toxicity of 213Bi- versus 90Y-labeled CO17-1A Fab′ fragments in a human colonic cancer model. Cancer Res. 59:2635-2643. - PubMed
-
- Dadachova, E., R. W. Howell, R. A. Bryan, A. Frenkel, J. D. Nosanchuk, and A. Casadevall. Susceptibility of human pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans and Histoplasma capsulatum to gamma radiation versus radioimmunotherapy with alpha- and beta-emitting radioisotopes. J. Nucl. Med., in press. - PubMed
-
- Knox, S. J., and R. F. Meredith. 2000. Clinical radioimmunotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 10:73-93. - PubMed
-
- Koenig, T. R., R. F. Munden, J. J. Erasmus, B. S. Sabloff, G. W. Gladish, R. Komaki, and C. W. Stevens. 2002. Radiation injury of the lung after three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 178:1383-1388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

