Role of attP in integrase-mediated integration of the Shigella resistance locus pathogenicity island of Shigella flexneri
- PMID: 14982801
- PMCID: PMC353151
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.3.1028-1031.2004
Role of attP in integrase-mediated integration of the Shigella resistance locus pathogenicity island of Shigella flexneri
Abstract
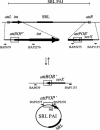
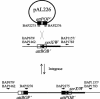
The Shigella resistance locus (SRL) pathogenicity island (PAI) in Shigella spp. mediates resistance to streptomycin, ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline. It can be excised from the chromosome via site-specific recombination mediated by the P4-related int gene. Here, we show that SRL PAI attP is capable of RecA-independent, site-specific, int-mediated integration into two bacterial tRNA attB sites.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nested deletions of the SRL pathogenicity island of Shigella flexneri 2a.J Bacteriol. 2001 Oct;183(19):5535-43. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.19.5535-5543.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11544215 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated site-specific recombination of the she pathogenicity island of Shigella flexneri.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Jun;52(5):1329-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04048.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15165236
-
Serotype conversion of a Shigella flexneri candidate vaccine strain via a novel site-specific chromosome-integration system.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998 Sep 1;166(1):79-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13186.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998. PMID: 9741086
-
[Progress of φC31 integrase system in site-specific integration].Yi Chuan. 2011 Jun;33(6):567-75. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2011.00567. Yi Chuan. 2011. PMID: 21684861 Review. Chinese.
-
A chromosome map of Shigella flexneri with the loci related to pathogenicity.Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1994 Jan-Feb;(1):3-10. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1994. PMID: 8133848 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Excision of the Shigella resistance locus pathogenicity island in Shigella flexneri is stimulated by a member of a new subgroup of recombination directionality factors.J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(16):5551-4. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.16.5551-5554.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15292162 Free PMC article.
-
The genome of Shigella dysenteriae strain Sd1617 comparison to representative strains in evaluating pathogenesis.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015 Mar;362(5):fnv011. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv011. Epub 2015 Jan 28. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25743074 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance Dynamics in Chilean Shigella sonnei Strains Within Two Decades: Role of Shigella Resistance Locus Pathogenicity Island and Class 1 and Class 2 Integrons.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 4;12:794470. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.794470. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35185820 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary chromosomal attachment site and tandem integration of the mobilizable Salmonella genomic island 1.PLoS One. 2008 Apr 30;3(4):e2060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002060. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18446190 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation, integrase-dependent excision, and horizontal transfer of genomic islands in Legionella pneumophila.J Bacteriol. 2013 Apr;195(7):1583-97. doi: 10.1128/JB.01739-12. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23354744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd, D., G. A. Peters, A. Cloeckaert, K. S. Boumedine, E. Chaslus-Dancla, H. Imberechts, and M. R. Mulvey. 2001. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 43-kilobase genomic island associated with the multidrug resistance region of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 and its identification in phage type DT120 and serovar Agona. J. Bacteriol. 183:5725-5732. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyd, D. A., G. A. Peters, L.-K. Ng, and M. R. Mulvey. 2000. Partial characterization of a genomic island associated with the multidrug resistance region of Salmonella enterica Typhymurium DT104. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 189:285-291. - PubMed
-
- Davis, B. M., and M. K. Waldor. 2002. Mobile genetic elements and bacterial pathogenesis, p. 1040-1059. In N. L. Craig, R. Craigie, M. Gellert, and A. M. Lambowitz (ed.), Mobile DNA II. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

