Inhibition of beta-lactamase II of Bacillus cereus by penamaldic derivatives of penicillins
- PMID: 14982810
- PMCID: PMC353088
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.3.1058-1060.2004
Inhibition of beta-lactamase II of Bacillus cereus by penamaldic derivatives of penicillins
Abstract
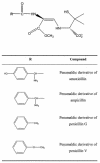
The penamaldic derivatives of amoxicillin, ampicillin, and penicillins G and V, stabilized with Zn(2+), were obtained from a methanolic medium. The enzymatic kinetic results show that the these derivatives elicit reversible inhibition of the enzyme metallo-beta-lactamase from Bacillus cereus, with inhibition constant values determined at pH 7.0 and 25 degrees C.
Figures

References
-
- Bounaga, S., M. Galleni, A. P. Laws, and M. I. Page. 2001. Cysteinyl peptide inhibitors of Bacillus cereus zinc β-lactamase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9:503-510. - PubMed
-
- Bush, K. 1998. Metallo-β-lactamases: a class apart. Clin. Infect. Dis. 27:48-53. - PubMed
-
- Davis, A. M., N. J. Layland, M. I. Page, F. Martin, and R. M. O'Ferrall. 1991. Thiazolidine ring opening in penicillin derivatives. Part 2. Enamine formation. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. II 1991:1225-1229.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

