Activities of dalbavancin in vitro and in a rabbit model of experimental endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus with or without reduced susceptibility to vancomycin and teicoplanin
- PMID: 14982811
- PMCID: PMC353077
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.3.1061-1064.2004
Activities of dalbavancin in vitro and in a rabbit model of experimental endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus with or without reduced susceptibility to vancomycin and teicoplanin
Abstract
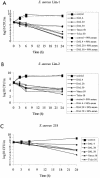
For the treatment of rabbit endocarditis, dalbavancin given once daily (10 mg/kg of body weight for 4 days) or as a single 40-mg/kg dose was active against Staphylococcus aureus with or without reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides, as expected from its good in vitro activity, even in broth supplemented with 90% serum and given its prolonged elimination half-life.
Figures

References
-
- Candiani, G., M. Abbondi, M. Borgonovi, M. Romano, and F. Parenti. 1999. In-vitro and in-vivo antibacterial activity of BI-397, a new semi-synthetic glycopeptide antibiotic. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 44:179-192. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1997. Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin—United States 1997. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 46:765-766. - PubMed
-
- Hiramatsu, K., H. Hanaki, T. Ino, K. Yabuta, T. Oguri, and F. C. Tenover. 1997. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strain with reduced vancomycin susceptibility. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 40:135-136. - PubMed
-
- Jones, R. N., D. J. Biedenbach, D. M. Johnson, and M. A. Pfaller. 2001. In vitro evaluation of BI-397, a novel glycopeptide antimicrobial agent. J. Chemother. 13:244-254. - PubMed
-
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2001. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 5th ed. Approved standard M7-A5. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

