Attenuation of Th1 effector cell responses and susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in histamine H2 receptor knockout mice is due to dysregulation of cytokine production by antigen-presenting cells
- PMID: 14982842
- PMCID: PMC1614706
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63176-8
Attenuation of Th1 effector cell responses and susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in histamine H2 receptor knockout mice is due to dysregulation of cytokine production by antigen-presenting cells
Abstract
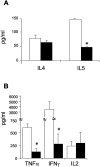
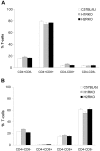
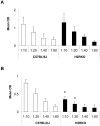
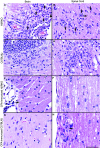
Histamine, a biogenic amine with both neurotransmitter and vasoactive properties, is well recognized as an immunomodulatory agent in allergic and inflammatory reactions. It also plays a regulatory role in the development of antigen-specific immune responses. CD4+ T-cells from histamine H1 receptor (H1R)-deficient (H1RKO) mice produce significantly less interferon-gamma and more interleukin (IL)-4 in in vitro recall assays compared to wild-type controls. H1RKO mice are also less susceptible to acute early-phase experimental allergic encephalomyelitis indicating that H1R signaling in CD4+ T cells plays a central role in regulating pathogenic T-cell responses. In this study, we show that mice lacking histamine H2 receptor (H2RKO) are similar to H1RKO mice in that they develop encephalitogen-specific T-cell responses as assessed by proliferation and IL-2 production and present with less severe acute early-phase experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. However, unlike T cells from H1RKO mice, which exhibit a strong Th2 bias, T cells from H2RKO mice do not. Rather, they are uniquely characterized by a significant inhibition of Th1 effector cell responses. Given that both histamine and adjuvants such as pertussis toxin modulate antigen-presenting cell (APC) maturation and function, including T-cell-polarizing activity, we analyzed the cytokines/chemokines secreted by APCs from wild-type, H1RKO, and H2RKO mice. Significant differences in cytokine/chemokine production by APCs from unimmunized and immunized mice were delineated. APCs from H2RKO mice produce significantly less IL-12 and IL-6 and markedly greater amounts of MCP-1 compared to wild-type and H1RKO mice. Because MCP-1 is known to inhibit IL-12 production, the failure of H2RKO mice to generate encephalitogenic Th1 effector cell responses is consistent with inhibition of negative regulation of MCP-1 secretion by H2R signaling in APCs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Histamine H₂ receptor signaling × environment interactions determine susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.FASEB J. 2014 Apr;28(4):1898-909. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-239939. Epub 2013 Dec 26. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24371118 Free PMC article.
-
The central nervous system environment controls effector CD4+ T cell cytokine profile in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Nov;27(11):2840-7. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830271115. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9394808
-
Systemic lack of canonical histamine receptor signaling results in increased resistance to autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2013 Jul 15;191(2):614-22. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203137. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23772030 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: cytokines, effector T cells, and antigen-presenting cells in a prototypical Th1-mediated autoimmune disease.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2003 Jan;3(1):86-93. doi: 10.1007/s11882-003-0017-6. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2003. PMID: 12543000 Review.
-
Effects of histamine on Th1/Th2 cytokine balance.Int Immunopharmacol. 2003 Jul;3(7):909-20. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5769(02)00235-7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12810348 Review.
Cited by
-
The histaminergic network in the brain: basic organization and role in disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Jul;14(7):472-87. doi: 10.1038/nrn3526. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23783198 Review.
-
Seasonal Changes in Serum Metabolites in Multiple Sclerosis Relapse.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3542. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043542. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834957 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 13;9:1873. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01873. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30150993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic and genomic characterisation of performance of tropically adapted chickens raised in smallholder farm conditions in Ethiopia.Front Genet. 2024 Apr 19;15:1383609. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1383609. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38706792 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor-1 (Esr1) and -2 (Esr2) regulate the severity of clinical experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in male mice.Am J Pathol. 2004 Jun;164(6):1915-24. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63752-2. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15161628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kapsenberg ML, Jansen HM, Bos JD, Wierenga EA. Role of type 1 and type 2 T helper cells in allergic disease. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992;4:788–793. - PubMed
-
- Sher A, Coffman RL. Regulation of immunity to parasite by T-cells and T-cell-derived cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:385–409. - PubMed
-
- Liblau RS, Springer SM, McDevitt HO. Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T-cells in the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Immunol Today. 1995;16:34–38. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond WM, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T-cell clones. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Mossman TT, Sad S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol Today. 1996;17:138–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

