Gene expression profiling identifies genes associated with invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas
- PMID: 14982844
- PMCID: PMC1613263
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63178-1
Gene expression profiling identifies genes associated with invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas
Abstract
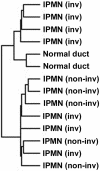
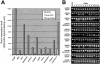
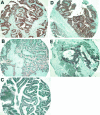
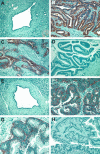
The molecular pathology of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas has not been well characterized, and there are no reliable markers to predict the presence of an associated invasive carcinoma in IPMNs. Using oligonucleotide microarrays, we performed a large-scale gene expression profiling of 12 IPMNs with or without an associated invasive carcinoma. A subset of genes identified was validated for the gene expression patterns in a large panel of IPMNs by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and/or immunohistochemistry. A total of 673 transcripts were identified as expressed at significantly higher levels (P < 0.05 and at fivefold or greater) in IPMNs relative to normal pancreatic ductal epithelial samples. Of interest, many of the genes identified as overexpressed in IPMNs have also been previously reported to be highly expressed in infiltrating ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. By analyzing genes overexpressed selectively in IPMNs with an associated invasive carcinoma (n = 7), we also identified a panel of genes potentially associated with the invasive phenotype of the neoplasms. Immunohistochemical validation revealed that claudin 4, CXCR4, S100A4, and mesothelin were expressed at significantly high frequency in invasive IPMNs than in noninvasive IPMNs. Notably, the expression of at least two of the four proteins was observed in 73% of 22 invasive IPMNs but in none of 16 noninvasive IPMNs (P < 0.0001). Our findings suggest that preoperative assessment of gene expression profiles may be able to differentiate invasive from noninvasive IPMNs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic down-regulation of CDKN1C/p57KIP2 in pancreatic ductal neoplasms identified by gene expression profiling.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jul 1;11(13):4681-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2471. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16000561
-
A genome-wide investigation of microRNA expression identifies biologically-meaningful microRNAs that distinguish between high-risk and low-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 21;10(1):e0116869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116869. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25607660 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression level of microRNA-196a is predictive of intestinal-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.Pancreas. 2014 Apr;43(3):361-6. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000042. Pancreas. 2014. PMID: 24622064
-
Epigenetic alterations in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006;13(4):280-5. doi: 10.1007/s00534-005-1056-2. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006. PMID: 16858538 Review.
-
Molecular genetics of intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007;14(3):233-7. doi: 10.1007/s00534-006-1167-4. Epub 2007 May 29. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007. PMID: 17520197 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of organoids derived from pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.J Pathol. 2020 Nov;252(3):252-262. doi: 10.1002/path.5515. Epub 2020 Sep 19. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32696980 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, class 2 beta (PI3KC2β) isoform contributes to neuroblastoma tumorigenesis.Cancer Lett. 2015 Apr 10;359(2):262-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.026. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25622909 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid characterization of candidate biomarkers for pancreatic cancer using cell microarrays (CMAs).J Proteome Res. 2012 Nov 2;11(11):5556-63. doi: 10.1021/pr300483r. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 22985314 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of S100A2 and S100A4 in lung adenocarcinomas: clinicopathological significance, relationship to p53 and identification of their target genes.Cancer Sci. 2005 Dec;96(12):844-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00121.x. Cancer Sci. 2005. PMID: 16367903 Free PMC article.
-
Glycomic Profiling Highlights Increased Fucosylation in Pseudomyxoma Peritonei.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 Nov;17(11):2107-2118. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000615. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30072579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohhashi K, Murakami F, Maruyama M. Four cases of mucous secreting pancreatic cancer. Prog Dig Endosc. 1982;203:348–351.
-
- Loftus EV, Jr, Olivares-Pakzad BA, Batts KP, Adkins MC, Stephens DH, Sarr MG, DiMagno EP. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas: clinicopathologic features, outcome, and nomenclature. Members of the Pancreas Clinic, and Pancreatic Surgeons of Mayo Clinic. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:1909–1918. - PubMed
-
- Adsay NV. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: pathology and molecular genetics. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002;6:656–659. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz-Winnenthal FH, Z’Graggen K, Volk C, Schmied BM, Buchler MW. Intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2003;5:133–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

