Intervertebral disc degeneration: the role of the mitochondrial pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload
- PMID: 14982845
- PMCID: PMC1613264
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63179-3
Intervertebral disc degeneration: the role of the mitochondrial pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload
Abstract
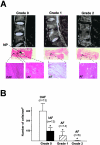
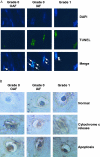
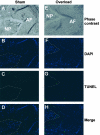
Degeneration of the intervertebral disk (IVD) is a major pathological process implicated in low back pain and is a prerequisite to disk herniation. Although mechanical stress is an important modulator of the degeneration, the underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear. The association of human IVD degeneration, assessed by magnetic resonance imaging, with annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis and anti-cytochrome c staining revealed that the activation of the mitochondria-dependent apoptosome was a major event in the degeneration process. Mouse models of IVD degeneration were used to investigate the role of the mechanical stress in this process. The application of mechanical overload (1.3 MPa) for 24 hours induced annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis and led to severe degeneration of the mouse disks. Immunostaining revealed cytochrome c release but not Fas-L generation. The role of the caspase-9-dependent mitochondrial pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload was investigated further with the use of cultured rabbit IVD cells in a stretch device. Mechanical overload (15% area change) induced apoptosis with increased caspase-9 activity and decreased mitochondrial membrane potential. Furthermore, Z-LEHD-FMK, a caspase-9 inhibitor, but not Z-IETD-FMK, a caspase-8 inhibitor, attenuated the overload-induced apoptosis. Our results from human samples, mouse models, and annulus fibrosus culture experiments demonstrate that the mechanical overload-induced IVD degeneration is mediated through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in IVD cells.
Figures
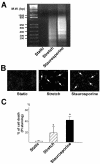

References
-
- Annunen S, Paassilta P, Lohiniva J, Perala M, Pihlajamaa T, Karppinen J, Tervonen O, Kroger H, Lahde S, Vanharanta H, Ryhanen L, Goring HH, Ott J, Prockop DJ, Ala-Kokko L. An allele of COL9A2 associated with intervertebral disc disease. Science. 1999;285:409–412. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Osada R, Kanamori M, Ishihara H, Ohmori K, Matsui H, Kimura T. Association between an aggrecan gene polymorphism and lumbar disc degeneration. Spine. 1999;24:2456–2460. - PubMed
-
- Hoogendoorn WE, van Poppel MNM, Bongers PM, Koes BW, Bouter LM. Systematic review of psychosocial factors at work and private life as risk factors for back pain. Spine. 2000;25:2114–2125. - PubMed
-
- Paassilta P, Lohiniva J, Goring HH, Perala M, Raina SS, Karppinen J, Hakala M, Palm T, Kroger H, Kaitila I, Vanharanta H, Ott J, Ala-Kokko L. Identification of a novel common genetic risk factor for lumbar disk disease. JAMA. 2001;285:1843–1849. - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Burton AK, Vogel S, Field AP. A systematic review of psychological factors as predictors of chronicity/disability in prospective cohorts of low back pain. Spine. 2002;27:109–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

