Lipoxins inhibit Akt/PKB activation and cell cycle progression in human mesangial cells
- PMID: 14982847
- PMCID: PMC1614708
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63181-1
Lipoxins inhibit Akt/PKB activation and cell cycle progression in human mesangial cells
Abstract
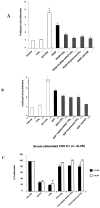
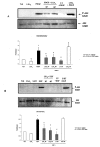
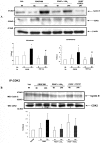
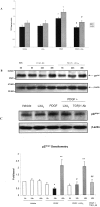
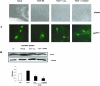
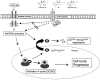
Lipoxins (LX) are endogenously produced eicosanoids with a spectrum of bioactions that suggest anti-inflammatory, pro-resolution roles for these agents. Mesangial cell (MC) proliferation plays a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of glomerular inflammation and is coupled to sclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. We have previously reported that LXA4 acts through a specific G-protein-coupled-receptor (GPCR) to modulate MC proliferation in response to the proinflammatory mediators LTD4 and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Further investigations revealed that these effects were mediated by modulation of receptor tyrosine kinase activity. Here we have explored the underlying mechanisms and report inhibition of growth factor (PDGF; epithelial growth factor) activation of Akt/PKB by LXA4. LXA4 (10 nmol/L) modulates PDGF-induced (10 ng/ml, 24 hours) decrements in the levels of cyclin kinase inhibitors p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. PDGF-induced increases in CDK2-cyclin E complex formation are also inhibited by LXA4. The potential of LXA4 as an anti-inflammatory therapeutic is compromised by its degradation; this has been circumvented by synthesis of stable analogs. We report that 15-(R/S)-methyl-LXA4 and 16-phenoxy-LXA4 mimic the native compound with respect to modulation of cell proliferation and PDGF-induced changes in cell cycle proteins. In vivo, MC proliferation in response to PDGF is associated with TGFbeta1 production and the subsequent development of renal fibrosis. Here we demonstrate that prolonged (24 to 48 hours) exposure to PDGF is associated with autocrine TGFbeta1 production, which is significantly reduced by LXA4. In aggregate these data demonstrate that LX inhibit PDGF stimulated proliferation via modulation of the PI-3-kinase pathway preventing mitogen-elicited G1-S phase progression and suggest the therapeutic potential of LX as anti-fibrotic agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipoxin A4 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced production of interleukins and proliferation of rat mesangial cells.Kidney Int. 2005 Jul;68(1):35-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00379.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 15954894
-
Aldose reductase regulates platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation through mediating cell cycle progression in rat mesangial cells.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Aug;30(2):409-16. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.997. Epub 2012 May 14. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22614447
-
Glucocorticoids stimulate p21(CIP1) in mesangial cells and in anti-GBM glomerulonephritis.Kidney Int. 2001 May;59(5):1706-16. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.0590051706.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11318941
-
Multiple roles of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression.Cell Cycle. 2003 Jul-Aug;2(4):339-45. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 12851486 Review.
-
Lipid-derived mediators in endogenous anti-inflammation and resolution: lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins.ScientificWorldJournal. 2002 Jan 22;2:169-204. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2002.81. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002. PMID: 12806051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trifluoperazine Inhibits Mesangial Cell Proliferation by Arresting Cell Cycle-Dependent Mechanisms.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Jul 17;23:3461-3469. doi: 10.12659/msm.902522. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28713151 Free PMC article.
-
D-series resolvin attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell activation and neointimal hyperplasia following vascular injury.FASEB J. 2013 Jun;27(6):2220-32. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-225615. Epub 2013 Feb 13. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23407709 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinogenesis: Failure of resolution of inflammation?Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Feb;218:107670. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107670. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32891711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators: Modulation of Diabetes-Associated Cardio-, Reno-, and Retino-Vascular Complications.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Dec 19;9:1488. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01488. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30618774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-resolving lipid mediators: regulators of inflammation, metabolism and kidney function.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Nov;17(11):725-739. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00454-y. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34282342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McMahon BM, Mitchell S, Brady HR, Godson C. Lipoxins: revelations on resolution. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:391–395. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN. Lipoxins and novel aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins[ATL]: a jungle of cell-cell interactions or a therapeutic opportunity? Prostaglandins. 1997;53:107–137. - PubMed
-
- Levy BD, Clish CB, Schmidt B, Gronert K, Serhan CN. Lipid mediator class switching during acute inflammation: signals in resolution. Nat Med. 2001;2:612–619. - PubMed
-
- Papayianni A, Serhan CN, Phillips ML, Rennke HG, Brady HR. Transcellular biosynthesis of lipoxin A4 during adhesion of platelets and neutrophils in experimental immune complex glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1995:1295–1302. - PubMed
-
- Mayadas TN, Mendrick DL, Brady HR, Tang T, Papayianni A, Assmann KJ, Wagner DD, Hynes RO, Cotran RS. Acute passive anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis in P-selectin-deficient mice. Kidney Int. 1996;49:1342–1349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

