Intracellular accumulation of amyloidogenic fragments of amyloid-beta precursor protein in neurons with Niemann-Pick type C defects is associated with endosomal abnormalities
- PMID: 14982851
- PMCID: PMC1614713
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63185-9
Intracellular accumulation of amyloidogenic fragments of amyloid-beta precursor protein in neurons with Niemann-Pick type C defects is associated with endosomal abnormalities
Erratum in
- Am J Pathol. 2004 Oct;165(4):1447
Abstract
Niemann-Pick type C disease (NPC) is characterized by neurodegeneration secondary to impaired cholesterol trafficking and excessive glycosphingolipid storage. Abnormal cholesterol and ganglioside metabolism may influence the generation and aggregation of amyloidogenic fragments (ie, C99 and Abeta) from amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP), crucial factors causing neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. To reveal whether abnormal accumulation and aggregation of APP fragments also occurs in NPC, we studied their expression in cultured cortical neurons treated with U18666A, a compound widely used to induce NPC defects, and also in brain tissues from NPC patients. U18666A treatment resulted in increased intraneuronal levels of C99 and insoluble Abeta42, which were distributed among early and late endosomes, in compartments distinct from where endogenous cholesterol accumulates. Analyses of NPC brains revealed that C99 or other APP C-terminal fragments (APP-CTF), but not Abeta42, accumulated in Purkinje cells, mainly in early endosomes. In contrast, in hippocampal pyramidal neurons, the major accumulated species was Abeta42, in late endosomes. Similar to what has been shown in Alzheimer's disease, cathepsin D, a lysosomal hydrolase, was redistributed to early endosomes in NPC Purkinje cells, where it co-localized with C99/APP-CTF. Our results suggest that endosomal abnormalities related to abnormal lipid trafficking in NPC may contribute to abnormal APP processing and Abeta42/C99/APP-CTF deposition.
Figures

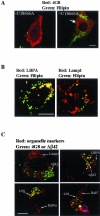

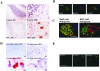
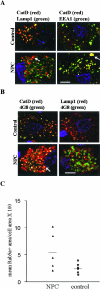
Comment in
-
Niemann-Pick Type C disease and Alzheimer's disease: the APP-endosome connection fattens up.Am J Pathol. 2004 Mar;164(3):757-61. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63163-X. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 14982829 Free PMC article. Review.
Similar articles
-
Niemann-Pick Type C disease and Alzheimer's disease: the APP-endosome connection fattens up.Am J Pathol. 2004 Mar;164(3):757-61. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63163-X. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 14982829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol-depletion corrects APP and BACE1 misstrafficking in NPC1-deficient cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1822(8):1270-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22551668
-
Accumulation and aggregation of amyloid beta-protein in late endosomes of Niemann-pick type C cells.J Biol Chem. 2001 Feb 9;276(6):4454-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009598200. Epub 2000 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11085995
-
APP overexpression in the absence of NPC1 exacerbates metabolism of amyloidogenic proteins of Alzheimer's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Dec 15;24(24):7132-50. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv413. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26433932 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanism of U18666A-mediated apoptosis in cultured murine cortical neurons: bridging Niemann-Pick disease type C and Alzheimer's disease.Cell Signal. 2006 Nov;18(11):1844-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.04.006. Epub 2006 May 7. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16797161 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol-dependent energy transfer between fluorescent proteins-insights into protein proximity of APP and BACE1 in different membranes in Niemann-Pick type C disease cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 26;13(12):15801-12. doi: 10.3390/ijms131215801. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23443094 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick Type C disease and Alzheimer's disease: the APP-endosome connection fattens up.Am J Pathol. 2004 Mar;164(3):757-61. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63163-X. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 14982829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol in Niemann-Pick Type C disease.Subcell Biochem. 2010;51:319-35. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-8622-8_11. Subcell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20213549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic epitopes are incorporated into age-dependent neurofibrillary tangles in Niemann-Pick disease type C.Brain Pathol. 2010 Mar;20(2):367-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00286.x. Epub 2009 May 20. Brain Pathol. 2010. PMID: 19476463 Free PMC article.
-
A Unified Hypothesis of Early- and Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47(1):33-47. doi: 10.3233/JAD-143210. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26402752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liscum L, Klansek JJ. Niemann-Pick disease type C. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1998;9:131–135. - PubMed
-
- Strauss JF, Liu P, Christenson LK, Watari H. Sterols and intracellular vesicular trafficking: lessons from the study of NPC1. Steroids. 2002;67:947–951. - PubMed
-
- Vanier MT, Suzuki K. Niemann-Pick disease. Moser HW, editor. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science,; Handbook of Clinical NeurologyNeurodystrophies and Neurolipidosis. 1996:pp 132–162.
-
- Liscum L. Niemann-Pick type C mutations cause lipid traffic jam. Traffic. 2000;1:218–225. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S, Maxfield FR. Cholesterol: stuck in traffic. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:E37–E38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

