Multiple structural and functional abnormalities in the p450 aromatase expressing transgenic male mice are ameliorated by a p450 aromatase inhibitor
- PMID: 14982857
- PMCID: PMC1614717
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63191-4
Multiple structural and functional abnormalities in the p450 aromatase expressing transgenic male mice are ameliorated by a p450 aromatase inhibitor
Abstract
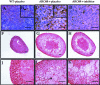
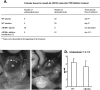
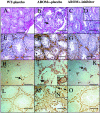
The present study was undertaken to analyze the effect of a P450 aromatase inhibitor (finrozole) on 4-month-old transgenic mice expressing human P450 aromatase (P450arom) under the human ubiquitin C promoter (AROM+). AROM+ mice present several dysfunctions, such as adrenal and pituitary hyperplasia, cryptorchidism, Leydig cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia, and gynecomastia. The present study demonstrates that these abnormalities were efficiently treated by administration of a P450arom inhibitor, finrozole. The treatment normalized the reduced intratesticular and serum testosterone levels, while those of estradiol were decreased. The body weight and several affected organ weights were normalized with the treatment. Histological analysis revealed that both the pituitary and adrenal hyperplasia were diminished. Furthermore, the cryptorchid testes present in the untreated AROM+ males descended to scrotum, 4 to 15 days after inhibitor treatment. In addition, the disrupted spermatogenesis was recovered and qualitatively complete spermatogenesis appeared with the inhibitor treatment. This was associated with normalized structure of the interstitial tissue, as analyzed by immunohistochemical staining for Leydig cells and macrophages. One of the features was that the Leydig cell hypertrophy was markedly diminished in the treated mice. AROM+ mice also present with severe gynecomastia, while the development and differentiation of the mammary gland in AROM+ males was markedly diminished with the inhibitor treatment. Interestingly, the mammary gland involution was associated with the induction of androgen receptor in the epithelial cells, while estrogen receptors were still detectable in the epithelium. The data show that AROM+ mouse model is a novel tool to further analyze the use of P450arom inhibitors in the treatment of the dysfunctions in males associated with misbalanced estrogen to androgen ratio, such as pituitary adenoma, testicular dysfunction, and gynecomastia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mammary gland development in transgenic male mice expressing human P450 aromatase.Endocrinology. 2002 Oct;143(10):4074-83. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220181. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 12239119
-
Phenotype characteristics of transgenic male mice expressing human aromatase under ubiquitin C promoter.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Sep;86(3-5):469-76. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00376-5. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14623546 Review.
-
Altered structure and function of reproductive organs in transgenic male mice overexpressing human aromatase.Endocrinology. 2001 Jun;142(6):2435-42. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.6.8211. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11356692
-
Transgenic mice expressing p450 aromatase as a model for male infertility associated with chronic inflammation in the testis.Endocrinology. 2006 Mar;147(3):1271-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0654. Epub 2005 Nov 23. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16306085
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of androstenedione (CAS No. 63-05-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010 Sep;(560):1, 7-31,33-171 passim. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010. PMID: 21037592 Review.
Cited by
-
NLRP3 in somatic non-immune cells of rodent and primate testes.Reproduction. 2018 Sep;156(3):231-238. doi: 10.1530/REP-18-0111. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Reproduction. 2018. PMID: 29907661 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: The androgen receptor in breast tissues: growth inhibitor, tumor suppressor, oncogene?Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Aug;26(8):1252-67. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1107. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22745190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory Effects of Estradiol and Its Mixtures with Ligands of GPER and PPAR on MAPK and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways and Tumorigenic Factors in Mouse Testis Explants and Mouse Tumor Leydig Cells.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 12;10(6):1390. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061390. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740412 Free PMC article.
-
An aroma of complexity: how the unique genetics of aromatase (CYP19A1) explain diverse phenotypes from hens and hyenas to human gynecomastia, and testicular and other tumors.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Dec;98(12):4676-81. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3990. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24311795 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sterile inflammation as a factor in human male infertility: Involvement of Toll like receptor 2, biglycan and peritubular cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 16;6:37128. doi: 10.1038/srep37128. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27849015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Means GD, Mahendroo MS, Corbin CJ, Mathis JM, Powell FE, Mendelson CR, Simpson ER. Structural analysis of the gene encoding human aromatase cytochrome P-450, the enzyme responsible for estrogen biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:19385–19391. - PubMed
-
- Thompson EA, Jr, Siiteri PK. The involvement of human placental microsomal cytochrome P-450 in aromatization. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:5373–5378. - PubMed
-
- Mendelson CR, Wright EE, Evans CT, Porter JC, Simpson ER. Preparation and characterization of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against human aromatase cytochrome P-450 (P-450AROM), and their use in its purification. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985;243:480–491. - PubMed
-
- Henderson IC, Canellos GP. Cancer of the breast: the past decade (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980;302:78–90. - PubMed
-
- Miller WR. Aromatase activity in breast tissue. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;39:783–790. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

