The plasminogen activation system reduces fibrosis in the lung by a hepatocyte growth factor-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 14982862
- PMCID: PMC1614722
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63196-3
The plasminogen activation system reduces fibrosis in the lung by a hepatocyte growth factor-dependent mechanism
Abstract
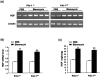
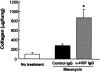
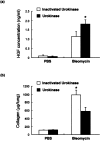
Mice deficient in the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene (PAI-1-/- mice) are relatively protected from developing pulmonary fibrosis from bleomycin administration. We hypothesized that one of the protective mechanisms may be the ability of the plasminogen system to enhance hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) effects, which have been reported to be anti-fibrotic in the lung. HGF is known to be sequestered in tissues by binding to extracellular matrix components. Following bleomycin administration, we found that HGF protein levels were higher in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from PAI-1-/- mice compared to wild-type (PAI-1+/+) mice. This increase could be suppressed by administering tranexamic acid, which inhibits plasmin activity. Conversely, intratracheal instillation of urokinase into bleomycin-injured PAI-1+/+ mice to activate plasminogen caused a significant increase in HGF within bronchoalveolar lavage and caused less collagen accumulation in the lungs. Administration of an anti-HGF neutralizing antibody markedly increased collagen accumulation in the lungs of bleomycin-injured PAI-1-/- mice. These results support the hypothesis that increasing the availability of HGF, possibly by enhancing its release from extracellular matrix by a plasmin-dependent mechanism, is an important means by which activation of the plasminogen system can limit pulmonary fibrosis.
Figures
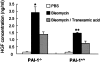

Similar articles
-
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in fibrinogen-null mice.J Clin Invest. 2000 Dec;106(11):1341-50. doi: 10.1172/JCI10531. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11104787 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen-mediated activation and release of hepatocyte growth factor from extracellular matrix.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Dec;35(6):705-13. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0006OC. Epub 2006 Jul 13. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16840775 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by RNA interference attenuates pulmonary fibrosis.Thorax. 2010 Apr;65(4):334-40. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.119974. Thorax. 2010. PMID: 20388759
-
The role of urokinase in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and implication for therapy.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Jun;17(6):905-16. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.6.905. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18491991 Review.
-
The fibrogenic actions of the coagulant and plasminogen activation systems in pulmonary fibrosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;97:108-117. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29474926 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV regulates immune function-related gene expression in human monocytic cells.Viral Immunol. 2012 Aug;25(4):277-88. doi: 10.1089/vim.2011.0099. Viral Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22876772 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Dec;27(6):600-12. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-957332. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 17195137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental regulation of inflammatory cytokine-mediated Stat3 signaling: the missing link between intrauterine growth restriction and pulmonary dysfunction?J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Aug;90(8):945-57. doi: 10.1007/s00109-012-0860-9. Epub 2012 Jan 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22271168
-
Always cleave up your mess: targeting collagen degradation to treat tissue fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Jun 1;304(11):L709-21. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00418.2012. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23564511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urokinase and its receptors in chronic kidney disease.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:5462-78. doi: 10.2741/3093. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuhn C, 3rd, Boldt J, King TE, Jr, Crouch E, Vartio T, McDonald JA. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;140:1693–1703. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn C. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Monogr Pathol. 1993:78–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

