The Bik BH3-only protein is induced in estrogen-starved and antiestrogen-exposed breast cancer cells and provokes apoptosis
- PMID: 14983013
- PMCID: PMC356954
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307337101
The Bik BH3-only protein is induced in estrogen-starved and antiestrogen-exposed breast cancer cells and provokes apoptosis
Abstract
Evidence has been accumulating that some estrogen-dependent human breast cancers require estrogen for not only proliferation but also survival. To obtain insights into the molecular mechanisms of apoptosis of breast cancer cells subjected to estrogen starvation or exposed to antiestrogens, we characterized changes in the gene expression profile of MCF-7/BUS human breast cancer cells and revealed a strong induction of Bik, a member of the BH3-only proapoptotic proteins. The Bik mRNA transcript and protein were strongly induced by estrogen starvation or exposure to fulvestrant, a pure antiestrogen that competes with the natural estrogens for binding to the estrogen receptors. This Bik induction preceded apoptotic cell death, which was blocked by zVAD-fmk, a pancaspase inhibitor. Amounts of the Bcl-2-related proteins, such as Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, or Bax, showed only marginal changes in the presence or absence of estrogens or antiestrogens. Suppression of Bik expression by using the small interfering RNA effectively blocked the fulvestrant-induced breast cancer cell apoptosis. These results indicate that Bik is induced in MCF-7/BUS cells in the absence of estrogen signaling and plays a critical role in the antiestrogen-provoked breast cancer cell apoptosis.
Figures
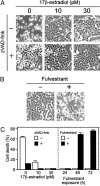

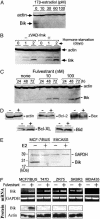
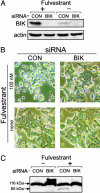
References
-
- Sommer, S. & Fuqua, S. A. (2001) Semin. Cancer Biol. 11, 339–352. - PubMed
-
- Thiantanawat, A., Long, B. J. & Brodie, A. M. (2003) Cancer Res. 63, 8037–8050. - PubMed
-
- Bursch, W., Ellinger, A., Kienzl, H., Torok, L., Pandey, S., Sikorska, M., Walker, R. & Hermann, R. S. (1996) Carcinogenesis 17, 1595–1607. - PubMed
-
- Ellis, P. A., Saccani-Jotti, G., Clarke, R., Johnston, S. R., Anderson, E., Howell, A., A'Hern, R., Salter, J., Detre, S., Nicholson, R., et al. (1997) Int. J. Cancer 72, 608–613. - PubMed
-
- Kandouz, M., Lombet, A., Perrot, J. Y., Jacob, D., Carvajal, S., Kazem, A., Rostene, W., Therwath, A. & Gompel, A. (1999) J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 69, 463–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

