A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors
- PMID: 14985473
- PMCID: PMC390315
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh040
A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors
Abstract
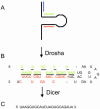
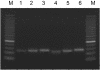
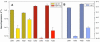
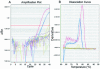
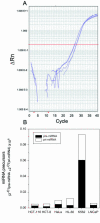
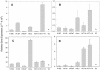
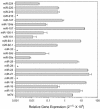
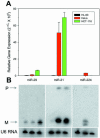
microRNAs (miRNAs) are small, functional, non-coding RNAs. miRNAs are transcribed as long primary transcripts (primary precursors) that are processed to the approximately 75 nt precursors (pre-miRNAs) by the nuclear enzyme Drosha. The approximately 22 nt mature miRNA is processed from the pre-miRNA by the RNase III Dicer. The vast majority of published studies to date have used northern blotting to detect the expression of miRNAs. We describe here a sensitive, high throughput, real-time PCR assay to monitor the expression of miRNA precursors. Gene-specific primers and reverse transcriptase were used to convert the primary precursors and pre-miRNAs to cDNA. The expression of 23 miRNA precursors in six human cancer cell lines was assayed using the PCR assay. The miRNA precursors accumulated to different levels when compared with each other or when a single precursor is compared in the various cell lines. The precursor expression profile of three miRNAs determined by the PCR assay was identical to the mature miRNA expression profile determined by northern blotting. We propose that the PCR assay may be scaled up to include all of the 150+ known human miRNA genes and can easily be adaptable to other organisms such as plants, Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila.
Figures

References
-
- Pasquinelli A.E. and Ruvkun,G. (2002) Control of developmental timing by microRNAs and their targets. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol., 18, 495–513. - PubMed
-
- Moss E.G. and Poethig,R.S. (2002) MicroRNAs: something new under the sun. Curr. Biol., 12, R688–R690. - PubMed
-
- Grishok A., Pasquinelli,A.E., Conte,D., Li,N., Parrish,S., Ha,I., Baillie,D.L., Fire,A., Ruvkun,G. and Mello,C.C. (2001) Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C.elegans developmental timing. Cell, 106, 23–34. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G., McLachlan,J., Pasquinelli,A.E., Balint,E., Tuschl,T. and Zamore,P.D. (2001) A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA. Science, 293, 834–838. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

