Relation of serial changes in childhood body-mass index to impaired glucose tolerance in young adulthood
- PMID: 14985484
- PMCID: PMC3408694
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa035698
Relation of serial changes in childhood body-mass index to impaired glucose tolerance in young adulthood
Abstract
Background: The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus is increased in people who have low birth weights and who subsequently become obese as adults. Whether their obesity originates in childhood and, if so, at what age are unknown. Understanding the origin of obesity may be especially important in developing countries, where type 2 diabetes is rapidly increasing yet public health messages still focus on reducing childhood "undernutrition."
Methods: We evaluated glucose tolerance and plasma insulin concentrations in 1492 men and women 26 to 32 years of age who had been measured at birth and at intervals of three to six months throughout infancy, childhood, and adolescence in a prospective, population-based study.
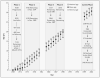
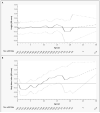
Results: The prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance was 10.8 percent, and that of diabetes was 4.4 percent. Subjects with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes typically had a low body-mass index up to the age of two years, followed by an early adiposity rebound (the age after infancy when body mass starts to rise) and an accelerated increase in body-mass index until adulthood. However, despite an increase in body-mass index between the ages of 2 and 12 years, none of these subjects were obese at the age of 12 years. The odds ratio for disease associated with an increase in the body-mass index of 1 SD from 2 to 12 years of age was 1.36 (95 percent confidence interval, 1.18 to 1.57; P<0.001).
Conclusions: There is an association between thinness in infancy and the presence of impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes in young adulthood. Crossing into higher categories of body-mass index after the age of two years is also associated with these disorders.
Copyright 2004 Massachusetts Medical Society
Figures
Comment in
-
Overweight in childhood and adolescence.N Engl J Med. 2004 Feb 26;350(9):855-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp048008. N Engl J Med. 2004. PMID: 14985480 No abstract available.
-
The changing face and implications of childhood obesity.N Engl J Med. 2004 Jun 3;350(23):2414-6; author reply 2414-6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200406033502317. N Engl J Med. 2004. PMID: 15175446 No abstract available.
-
The changing face and implications of childhood obesity.N Engl J Med. 2004 Jun 3;350(23):2414-6; author reply 2414-6. N Engl J Med. 2004. PMID: 15179696 No abstract available.
-
The changing face and implications of childhood obesity.N Engl J Med. 2004 Jun 3;350(23):2414-6; author reply 2414-6. N Engl J Med. 2004. PMID: 15179697 No abstract available.
References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:1414–31. - PubMed
-
- Pradeepa R, Mohan V. The changing scenario of the diabetes epidemic: implications for India. Indian J Med Res. 2002;116:121–32. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Latha E, Vijay V, Viswanathan M. Rising prevalence of NIDDM in an urban population in India. Diabetologia. 1997;40:232–7. - PubMed
-
- Rich-Edwards JW, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, et al. Birthweight and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adult women. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:278–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
