Kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures
- PMID: 14986073
- PMCID: PMC3468137
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-003-0654-4
Kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures
Abstract
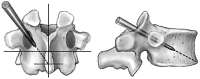
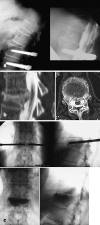
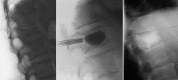
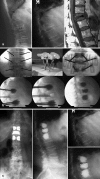
Cement reinforcement for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures is efficient mean with high success in pain release and prevention of further sintering of the reinforced vertebrae; however, the technique does not allow to address the kyphotic deformity. Kyphoplasty was designed to address the kyphotic deformity and help to realign the spine. It involves the percutaneous placement of an inflatable bone tamp into a vertebral body. Restoration of VB height and kyphosis correction is achieved by inflation of the bone tamp with liquid. After deflation, a cavity is created that eases the cement application. The potential of kyphosis reduction is given in fresh fractures with a range of 0-90% for height restoration and absolute correction of the kyphotic angle of 8.5 degrees. The cavity formation, on one hand, and the different cementing technique leads to lower risk for cement extravasation. An alternative method for kyphosis correction represents the so-called lordoplasty where the adjacent vertebrae are reinforced first and with the cannulas in place acting as a lever the reduction of the collapsed vertebra can be performed. The results with respect to kyphosis correction are superior in comparison with a kyphoplasty procedure.
Figures



Comment in
-
The Michel Benoist and Robert Mulholland yearly European Spine Journal review: a survey of the "surgical and research" articles in the European Spine Journal, 2005.Eur Spine J. 2006 Jan;15(1):8-15. doi: 10.1007/s00586-005-1062-8. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Eur Spine J. 2006. PMID: 16411129 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

