BDNF boosts spike fidelity in chaotic neural oscillations
- PMID: 14990508
- PMCID: PMC1304016
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74249-6
BDNF boosts spike fidelity in chaotic neural oscillations
Abstract
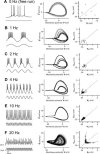
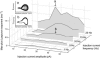
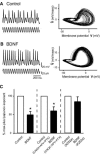
Oscillatory activity and its nonlinear dynamics are of fundamental importance for information processing in the central nervous system. Here we show that in aperiodic oscillations, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a member of the neurotrophin family, enhances the accuracy of action potentials in terms of spike reliability and temporal precision. Cultured hippocampal neurons displayed irregular oscillations of membrane potential in response to sinusoidal 20-Hz somatic current injection, yielding wobbly orbits in the phase space, i.e., a strange attractor. Brief application of BDNF suppressed this unpredictable dynamics and stabilized membrane potential fluctuations, leading to rhythmical firing. Even in complex oscillations induced by external stimuli of 40 Hz (gamma) on a 5-Hz (theta) carrier, BDNF-treated neurons generated more precisely timed spikes, i.e., phase-locked firing, coupled with theta-phase precession. These phenomena were sensitive to K252a, an inhibitor of tyrosine receptor kinases and appeared attributable to BDNF-evoked Na(+) current. The data are the first indication of pharmacological control of endogenous chaos. BDNF diminishes the ambiguity of spike time jitter and thereby might assure neural encoding, such as spike timing-dependent synaptic plasticity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emergence of chaotic attractor and anti-synchronization for two coupled monostable neurons.Chaos. 2004 Dec;14(4):1148-56. doi: 10.1063/1.1821691. Chaos. 2004. PMID: 15568928
-
Apamin-induced irregular firing in vitro and irregular single-spike firing observed in vivo in dopamine neurons is chaotic.Neuroscience. 2001;104(3):829-40. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00121-x. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11440813
-
Nonlinear dynamics of the membrane potential of a bursting pacemaker cell.Chaos. 2012 Mar;22(1):013123. doi: 10.1063/1.3687017. Chaos. 2012. PMID: 22462999
-
The theta/gamma discrete phase code occuring during the hippocampal phase precession may be a more general brain coding scheme.Hippocampus. 2005;15(7):913-22. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20121. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 16161035 Review.
-
Phase organization of network computations.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015 Apr;31:250-3. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25679370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired Reliability and Precision of Spiking in Adults But Not Juveniles in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.eNeuro. 2019 Dec 3;6(6):ENEURO.0217-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0217-19.2019. Print 2019 Nov/Dec. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31685673 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Therapeutic Mechanisms in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 29;23(15):8417. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158417. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuromodulation of spike-timing precision in sensory neurons.J Neurosci. 2006 May 31;26(22):5910-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4659-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16738233 Free PMC article.
-
Chronometric readout from a memory trace: gamma-frequency field stimulation recruits timed recurrent activity in the rat CA3 network.J Physiol. 2004 Nov 15;561(Pt 1):123-31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.066639. Epub 2004 Sep 16. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15375190 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal deletion of BDNF gene attenuates gamma oscillations in area CA1 by up-regulating 5-HT3 receptor.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 26;6(1):e16480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016480. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21298058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aihara, K., G. Matsumoto, and Y. Ikegaya. 1984. Periodic and non-periodic responses of a periodically forced Hodgkin-Huxley oscillator. J. Theor. Biol. 109:249–269. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J. M., W. M. Usrey, and R. C. Reid. 1996. Precisely correlated firing in cells of the lateral geniculate nucleus. Nature. 383:815–819. - PubMed
-
- Blum, R., K. W. Kafitz, and A. Konnerth. 2002. Neurotrophin-evoked depolarization requires the sodium channel Na(V)1.9. Nature. 419:687–693. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger, L., and M. Poo. 1999. Gating of BDNF-induced synaptic potentiation by cAMP. Science. 284:1982–1984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

