Local expression of B7-H1 promotes organ-specific autoimmunity and transplant rejection
- PMID: 14991067
- PMCID: PMC351315
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19210
Local expression of B7-H1 promotes organ-specific autoimmunity and transplant rejection
Abstract
A number of studies have suggested B7-H1, a B7 family member, inhibits T cell responses. Therefore, its expression on nonlymphoid tissues has been proposed to prevent T cell-mediated tissue destruction. To test this hypothesis, we generated transgenic mice that expressed B7-H1 on pancreatic islet beta cells. Surprisingly, we observed accelerated rejection of transplanted allogeneic B7-H1-expressing islet beta cells. Furthermore, transgenic B7-H1 expression broke immune tolerance, as some of the mice spontaneously developed T cell-dependent autoimmune diabetes. In addition, B7-H1 expression increased CD8+ T cell proliferation and promoted autoimmunity induction in a T cell adoptive transfer model of diabetes. Consistent with these findings, B7-H1.Ig fusion protein augmented naive T cell priming both in vitro and in vivo. Our results demonstrate that B7-H1 can provide positive costimulation for naive T cells to promote allograft rejection and autoimmune disease pathogenesis.
Figures
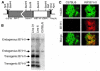
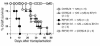
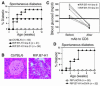
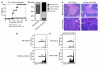
References
-
- Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat. Med. 1999;5:1365–1369. - PubMed
-
- Dong H, et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002;8:793–800. - PubMed
-
- Tamura H, et al. B7-H1 costimulation preferentially enhances CD28-independent T-helper cell function. Blood. 2001;97:1809–1816. - PubMed
-
- Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001;19:683–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

