Pathway for polyarginine entry into mammalian cells
- PMID: 14992581
- PMCID: PMC2819928
- DOI: 10.1021/bi035933x
Pathway for polyarginine entry into mammalian cells
Abstract
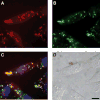
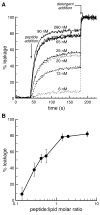
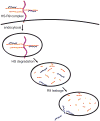
Cationic peptides known as protein transduction domains (PTDs) provide a means to deliver molecules into mammalian cells. Here, nonaarginine (R(9)), the most efficacious of known PTDs, is used to elucidate the pathway for PTD internalization. Although R(9) is found in the cytosol as well as the nucleolus when cells are fixed, this peptide is observed only in the endocytic vesicles of live cells. Colocalization studies with vesicular markers confirm that PTDs are internalized by endocytosis rather than by crossing the plasma membrane. The inability of R(9) to enter living cells deficient in heparan sulfate (HS) suggests that binding to HS is necessary for PTD internalization. This finding is consistent with the high affinity of R(9) for heparin (K(d) = 109 nM). Finally, R(9) is shown to promote the leakage of liposomes but only at high peptide:lipid ratios. These and other data indicate that the PTD-mediated delivery of molecules into live mammalian cells involves (1) binding to cell surface HS, (2) uptake by endocytosis, (3) release upon HS degradation, and (4) leakage from endocytic vesicles.
Figures



References
-
- Hallbrink M, Floren A, Elmquist A, Pooga M, Bartfai T, Langel U. Cargo delivery kinetics of cell-penetrating peptides. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2001;1515:101–109. - PubMed
-
- Denicourt C, Dowdy SF. Protein transduction technology offers novel therapeutic approach for brain ischemia. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:216–218. - PubMed
-
- Green I, Christison R, Voyce CJ, Bundell KR, Lindsay MA. Protein transduction domains: Are they delivering? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:213–215. - PubMed
-
- Leifert JA, Lindsay Whitton J. “Translocatory proteins” and “protein transduction domains”: A critical analysis of their biological effects and underlying mechanisms. Mol Ther. 2003;8:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Thierry AR, Vives E, Richard JP, Prevot P, Martinand-Mari C, Robbins I, Lebleu B. Cellular uptake and intracellular fate of antisense oligonucleotides. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2003;5:133–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

