Anti-inflammatory effect of diosmectite in hapten-induced colitis in the rat
- PMID: 14993105
- PMCID: PMC1574279
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705710
Anti-inflammatory effect of diosmectite in hapten-induced colitis in the rat
Abstract
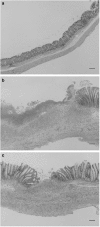
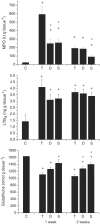
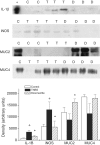
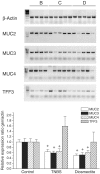
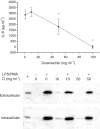
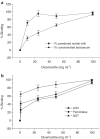
1. Diosmectite is a natural silicate effectively used in the treatment of infectious diarrhoea. Its antidiarrhoeal properties involve adsorption of toxins and bacteria and modifications of the rheological characteristics of gastrointestinal mucus. Hence, the aim of this study was to test the intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of diosmectite. 2. Diosmectite (500 mg x kg(-1) day(-1), p.o.) was administered as a post-treatment to rats with chronic trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid colitis. Colonic status was checked 1 and 2 weeks after colitis induction by macroscopic, histological and biochemical examination. 3. Diosmectite post-treatment resulted in amelioration of the morphological signs (intestinal weight, macroscopic damage, necrosed area, histology) and biochemical markers (myeloperoxidase activity, glutathione levels, MUC2 expression, inducible nitric oxide synthase and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and leukotriene B(4) synthesis), as well as in the reduction of the severity of diarrhoea. The effect of the clay was comparable to that of sulphasalazine (50 mg x kg(-1) day(-1)). 4. 5. Diosmectite exhibited a dose-dependent capacity to adsorb proteins in vitro as well as a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on the basolateral secretion of IL-8 by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated HT29 cells. Diosmectite had a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on IL-1beta production by LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells. 6. The effect of diosmectite on MUC2 was post-transcriptional, since mRNA levels were unaffected. However, diosmectite is able to upregulate MUC2 mRNA levels in HT29-MTX cells. 7. Diosmectite has anti-inflammatory activity administered as a post-treatment. Possible mechanisms include adsorption of luminal antigens, increase of colonic mucin levels and possibly a direct modulatory action of cytokine production by mucosal cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibiotic treatment with ampicillin accelerates the healing of colonic damage impaired by aspirin and coxib in the experimental colitis. Importance of intestinal bacteria, colonic microcirculation and proinflammatory cytokines.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;62(3):357-68. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21893697
-
Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of morin on chronic experimental colitis in the rat.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Dec;15(12):2027-39. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.01133.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11736735
-
Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of hydroalcoholic extracts of Phlomis purpurea L. and Phlomis lychnitis L. in the trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid model of rat colitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Apr 19;146(3):750-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.01.041. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23395625
-
Anti-diarrheal effects of diosmectite in the treatment of acute diarrhea in children: a review.Paediatr Drugs. 2009;11(2):89-99. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200911020-00001. Paediatr Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19301931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of anti-inflammatory effects of PPARgamma agonists?Gut. 2006 Aug;55(8):1067-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.089946. Gut. 2006. PMID: 16849341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotic co-supplementation with absorbent smectite for pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a secondary-data analysis of a randomized double-blind controlled trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 8;15:1276642. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1276642. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38405158 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Suppression of ELF4 in ulcerative colitis predisposes host to colorectal cancer.iScience. 2021 Feb 9;24(3):102169. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102169. eCollection 2021 Mar 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33665583 Free PMC article.
-
Present and Future Therapeutic Approaches to Barrier Dysfunction.Front Nutr. 2021 Oct 28;8:718093. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.718093. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34778332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geophagy among East African Chimpanzees: consumed soils provide protection from plant secondary compounds and bioavailable iron.Environ Geochem Health. 2019 Dec;41(6):2911-2927. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00366-8. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Environ Geochem Health. 2019. PMID: 31278584
-
Disturbances in metabolic, transport and structural genes in experimental colonic inflammation in the rat: a longitudinal genomic analysis.BMC Genomics. 2008 Oct 17;9:490. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-490. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18928539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADAMS R.B., PLANCHON S.M., ROCHE J.K. IFN-gamma modulation of epithelial barrier function. Time course, reversibility, and site of cytokine binding. J. Immunol. 1993;150:2356–2363. - PubMed
-
- AKERBOOM T.P., SIES H. Assay of glutathione, glutathione disulfide, and glutathione mixed disulfides in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:373–382. - PubMed
-
- ALBENGRES E., URIEN S., TILLEMENT J.P., OURY P., DECOURT S., FLOUVAT B., DRIEU K. Interactions between smectite, a mucus stabilizer, and acidic and basic drugs. In vitro and in vivo studies. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1985;28:601–605. - PubMed
-
- ASFAHA S., MACNAUGHTON W.K., APPLEYARD C.B., CHADEE K., WALLACE J.L. Persistent epithelial dysfunction and bacterial translocation after resolution of intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G635–G644. - PubMed
-
- BELL C.J., GALL D.G., WALLACE J.L. Disruption of colonic electrolyte transport in experimental colitis. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;268:G622–G630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

