In vitro targeting reveals intrinsic histone tail specificity of the Sin3/histone deacetylase and N-CoR/SMRT corepressor complexes
- PMID: 14993276
- PMCID: PMC355843
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.6.2364-2372.2004
In vitro targeting reveals intrinsic histone tail specificity of the Sin3/histone deacetylase and N-CoR/SMRT corepressor complexes
Abstract
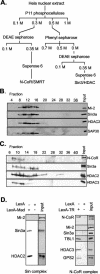
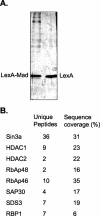
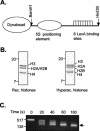
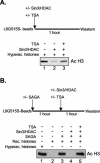
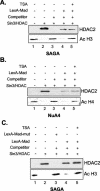
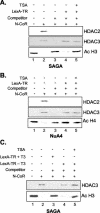
The histone code is among others established via differential acetylation catalyzed by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). To unambiguously determine the histone tail specificity of HDAC-containing complexes, we have established an in vitro system consisting of nucleosomal templates reconstituted with hyperacetylated histones or recombinant histones followed by acetylation with native SAGA or NuA4. Selective targeting of the mammalian Sin3/HDAC and N-CoR/SMRT corepressor complexes by using specific chimeric repressors created a near physiological setting to assess their histone tail specificity. Recruitment of the Sin3/HDAC complex to nucleosomal templates preacetylated with SAGA or NuA4 resulted in deacetylation of histones H3 and H4, whereas recruitment of N-CoR/SMRT resulted in deacetylation of histone H3 only. These results provide solid evidence that HDAC-containing complexes display distinct, intrinsic histone tail specificities and hence may function differently to regulate chromatin structure and transcription.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A feed-forward repression mechanism anchors the Sin3/histone deacetylase and N-CoR/SMRT corepressors on chromatin.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;26(14):5226-36. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00440-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16809761 Free PMC article.
-
Reading and function of a histone code involved in targeting corepressor complexes for repression.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(1):324-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.1.324-335.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15601853 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple N-CoR complexes contain distinct histone deacetylases.J Biol Chem. 2001 Mar 23;276(12):8807-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C000879200. Epub 2001 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11254656
-
N-CoR-HDAC corepressor complexes: roles in transcriptional regulation by nuclear hormone receptors.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;274:237-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55747-7_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12596910 Review.
-
Nuclear histone acetylases and deacetylases and transcriptional regulation: HATs off to HDACs.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1997 Oct;1(3):300-8. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(97)80066-x. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1997. PMID: 9667866 Review.
Cited by
-
Tristetraprolin represses estrogen receptor α transactivation in breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15554-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548552. Epub 2014 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24737323 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the functions and regulation of the transcriptional corepressors SMRT and N-CoR.Cell Div. 2009 Apr 21;4:7. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-4-7. Cell Div. 2009. PMID: 19383165 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro assay to study the recruitment and substrate specificity of chromatin modifying enzymes.Biol Proced Online. 2004;6:157-162. doi: 10.1251/bpo85. Epub 2004 Jul 27. Biol Proced Online. 2004. PMID: 15282629 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetylation and deacetylation - Mechanistic insights from structural biology.Gene. 2024 Jan 10;890:147798. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147798. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Gene. 2024. PMID: 37726026 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel CRISPR Interference Effector Enabling Functional Gene Characterization with Synthetic Guide RNAs.CRISPR J. 2022 Dec;5(6):769-786. doi: 10.1089/crispr.2022.0056. Epub 2022 Oct 17. CRISPR J. 2022. PMID: 36257604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayer, D. E., Q. A. Lawrence, and R. N. Eisenman. 1995. Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3. Cell 80:767-776. - PubMed
-
- Baek, S. H., K. A. Ohgi, D. W. Rose, E. H. Koo, C. K. Glass, and M. G. Rosenfeld. 2002. Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. Cell 110:55-67. - PubMed
-
- Becker, P. B., and W. Horz. 2002. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:247-273. - PubMed
-
- Bird, A. W., D. Y. Yu, M. G. Pray-Grant, Q. Qiu, K. E. Harmon, P. C. Megee, P. A. Grant, M. M. Smith, and M. F. Christman. 2002. Acetylation of histone H4 by Esa1 is required for DNA double-strand break repair. Nature 419:411-415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
