Nup358/RanBP2 attaches to the nuclear pore complex via association with Nup88 and Nup214/CAN and plays a supporting role in CRM1-mediated nuclear protein export
- PMID: 14993277
- PMCID: PMC355853
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.6.2373-2384.2004
Nup358/RanBP2 attaches to the nuclear pore complex via association with Nup88 and Nup214/CAN and plays a supporting role in CRM1-mediated nuclear protein export
Abstract
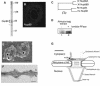
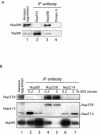
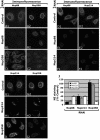
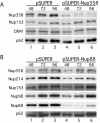
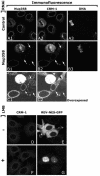
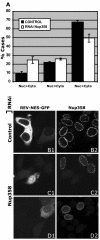
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) traverse the nuclear envelope (NE), providing a channel through which nucleocytoplasmic transport occurs. Nup358/RanBP2, Nup214/CAN, and Nup88 are components of the cytoplasmic face of the NPC. Here we show that Nup88 localizes midway between Nup358 and Nup214 and physically interacts with them. RNA interference of either Nup88 or Nup214 in human cells caused a strong reduction of Nup358 at the NE. Nup88 and Nup214 showed an interdependence at the NPC and were not affected by the absence of Nup358. These data indicate that Nup88 and Nup214 mediate the attachment of Nup358 to the NPC. We show that localization of the export receptor CRM1 at the cytoplasmic face of the NE is Nup358 dependent and represents its empty state. Also, removal of Nup358 causes a distinct reduction in nuclear export signal-dependent nuclear export. We propose that Nup358 provides both a platform for rapid disassembly of CRM1 export complexes and a binding site for empty CRM1 recycling into the nucleus.
Figures
References
-
- Agami, R., and R. Bernards. 2000. Distinct initiation and maintenance mechanisms cooperate to induce G1 cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. Cell 102:55-66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
