Absence of an essential role for thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor in murine B-cell development
- PMID: 14993294
- PMCID: PMC355866
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.6.2584-2592.2004
Absence of an essential role for thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor in murine B-cell development
Abstract
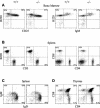
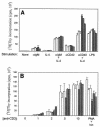
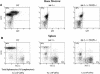
The murine cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) supports the development of B220+ IgM+ immature B cells and induces thymocyte proliferation in vitro. Human TSLP, by contrast, activates CD11c+ dendritic cells, but not B or T cells. Recent studies have demonstrated that the receptor for TSLP consists of a heterodimer of the interleukin 7 (IL-7) alpha chain and a novel protein that resembles the hematopoietic cytokine receptor common gamma chain. We examined signal transduction by the gamma-like chains using chimeric receptor proteins. The cytoplasmic domain of the human, but not of the murine, gamma-like chain, activates Jak2 and Stat5 and supports the proliferation of hematopoietic cell lines. In order to assess the role of the murine gamma-like chain in vivo, we generated gamma-like chain-deficient mice. Receptor-deficient mice are unresponsive to TSLP but exhibit no obvious phenotypic defects. In particular, hematopoietic cell development appeared normal. B-cell development, including the IgM+ compartment, was unaffected by loss of the TSLP pathway, as were T lymphopoiesis and lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. Cytokine receptors that utilize the common gamma chain signal through the lymphocyte-specific kinase Jak3. Mice deficient in Jak3 exhibit a SCID phenotype but harbor a residual B220+ splenic lymphocyte population. We demonstrate here that this residual lymphocyte population is lost in mice lacking both the gamma-like chain and Jak3.
Figures



References
-
- Blagoev, B., M. M. Nielsen, M. Angrist, A. Chakravarti, and A. Pandey. 2002. Cloning of rat thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor (TSLP-R) and characterization of genomic structure of murine Tslpr gene. Gene 284:161-168. - PubMed
-
- Friend, S. L., S. Hosier, A. Nelson, D. Foxworthe, D. E. Williams, and A. Farr. 1994. A thymic stromal cell line supports in vitro development of surface IgM+ B cells and produces a novel growth factor affecting B and T lineage cells. Exp. Hematol. 22:321-328. - PubMed
-
- Fujio, K., T. Nosaka, T. Kojima, T. Kawashima, T. Yahata, N. G. Copeland, D. J. Gilbert, N. A. Jenkins, K. Yamamoto, T. Nishimura, and T. Kitamura. 2000. Molecular cloning of a novel type 1 cytokine receptor similar to the common gamma chain. Blood 95:2204-2211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
