Toll-like receptors 9 and 3 as essential components of innate immune defense against mouse cytomegalovirus infection
- PMID: 14993594
- PMCID: PMC373494
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0400525101
Toll-like receptors 9 and 3 as essential components of innate immune defense against mouse cytomegalovirus infection
Abstract
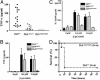
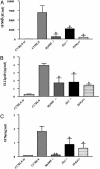
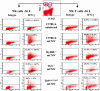
Several subsets of dendritic cells have been shown to produce type I IFN in response to viral infections, thereby assisting the natural killer cell-dependent response that eliminates the pathogen. Type I IFN production can be induced both by unmethylated CpG-oligodeoxynucleotide and by double-stranded RNA. Here, we describe a codominant CpG-ODN unresponsive phenotype that results from an N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea-induced missense mutation in the Tlr9 gene (Tlr9(CpG1)). Mice homozygous for the Tlr9(CpG1) allele are highly susceptible to mouse cytomegalovirus infection and show impaired infection-induced secretion of IFN-alpha/beta and natural killer cell activation. We also demonstrate that both the Toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 --> MyD88 and TLR3 --> Trif signaling pathways are activated in vivo on viral inoculation, and that each pathway contributes to innate defense against systemic viral infection. Whereas both pathways lead to type I IFN production, neither pathway offers full protection against mouse cytomegalovirus infection in the absence of the other. The Tlr9(CpG1) mutation alters a leucine-rich repeat motif and lies within a receptor domain that is conserved within the evolutionary cluster encompassing TLRs 7, 8, and 9. In other TLRs, including three mouse-specific TLRs described in this paper, the affected region is not represented. The phenotypic effect of the Tlr9(CpG1) allele thus points to a critical role for TLR9 in viral sensing and identifies a vulnerable amino acid within the ectodomain of three TLR proteins, essential for a ligand response.
Figures


References
-
- French, A. R. & Yokoyama, W. M. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 45-51. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. G., Dokun, A. O., Heusel, J. W., Smith, H. R., Beckman, D. L., Blattenberger, E. A., Dubbelde, C. E., Stone, L. R., Scalzo, A. A. & Yokoyama, W. M. (2001) Science 292, 934-937. - PubMed
-
- Lee, S. H., Girard, S., Macina, D., Busa, M., Zafer, A., Belouchi, A., Gros, P. & Vidal, S. M. (2001) Nat. Genet. 28, 42-45. - PubMed
-
- Arase, H., Mocarski, E. S., Campbell, A. E., Hill, A. B. & Lanier, L. L. (2002) Science 296, 1323-1326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

