Tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons is mediated by alpha5 subunit-containing gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors
- PMID: 14993607
- PMCID: PMC373519
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307231101
Tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons is mediated by alpha5 subunit-containing gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors
Abstract
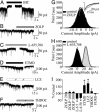
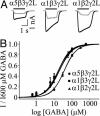
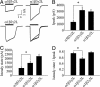
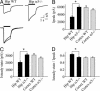
The principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), is thought to regulate memory processes by activating transient inhibitory postsynaptic currents. Here we describe a nonsynaptic, tonic form of inhibition in mouse CA1 pyramidal neurons that is generated by a distinct subpopulation of GABA type A receptors (GABA(A)Rs). This tonic inhibitory conductance is predominantly mediated by alpha5 subunit-containing GABA(A)Rs (alpha5GABA(A)Rs) that have different pharmacological and kinetic properties compared to postsynaptic receptors. GABA(A)Rs that mediate the tonic conductance are well suited to detect low, persistent, ambient concentrations of GABA in the extracellular space because they are highly sensitive to GABA and desensitize slowly. Moreover, the tonic current is highly sensitive to enhancement by amnestic drugs. Given the restricted expression of alpha5GABA(A)Rs to the hippocampus and the association between reduced alpha5GABA(A)R function and improved memory performance in behavioral studies, our results suggest that tonic inhibition mediated by alpha5GABA(A)Rs in hippocampal pyramidal neurons plays a key role in cognitive processes.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

