Venezuelan kindreds reveal that genetic and environmental factors modulate Huntington's disease age of onset
- PMID: 14993615
- PMCID: PMC373491
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0308679101
Venezuelan kindreds reveal that genetic and environmental factors modulate Huntington's disease age of onset
Abstract
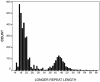
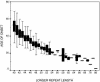
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease caused by a triplet (CAG) expansion mutation. The length of the triplet repeat is the most important factor in determining age of onset of HD, although substantial variability remains after controlling for repeat length. The Venezuelan HD kindreds encompass 18,149 individuals spanning 10 generations, 15,409 of whom are living. Of the 4,384 immortalized lymphocyte lines collected, 3,989 DNAs were genotyped for their HD alleles, representing a subset of the population at greatest genetic risk. There are 938 heterozygotes, 80 people with variably penetrant alleles, and 18 homozygotes. Analysis of the 83 kindreds that comprise the Venezuelan HD kindreds demonstrates that residual variability in age of onset has both genetic and environmental components. We created a residual age of onset phenotype from a regression analysis of the log of age of onset on repeat length. Familial correlations (correlation +/- SE) were estimated for sibling (0.40 +/- 0.09), parent-offspring (0.10 +/- 0.11), avuncular (0.07 +/- 0.11), and cousin (0.15 +/- 0.10) pairs, suggesting a familial origin for the residual variance in onset. By using a variance-components approach with all available familial relationships, the additive genetic heritability of this residual age of onset trait is 38%. A model, including shared sibling environmental effects, estimated the components of additive genetic (0.37), shared environment (0.22), and nonshared environment (0.41) variances, confirming that approximately 40% of the variance remaining in onset age is attributable to genes other than the HD gene and 60% is environmental.
Figures
References
-
- Bates, G., Harper, P. & Jones, L. (2002) Huntington's Disease (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford), 3rd Ed.
-
- Gusella, J. F., Wexler, N. S., Conneally, P. M., Naylor, S. L., Anderson, M. A., Tanzi, R. E., Watkins, P. C., Ottina, K., Wallace, M. R., Sakaguchi, A. Y., et al. (1983) Nature 306, 234-238. - PubMed
-
- The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group (1993) Cell 72, 971-983. - PubMed
-
- Feigin, A. & Zgaljardic, D. (2002) Curr. Opin. Neurol. 15, 483-489. - PubMed
-
- Ross, C. A. (2002) Neuron 35, 819-822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

