Mutational analysis of the signal-sensing domain of ResE histidine kinase from Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 14996800
- PMCID: PMC355969
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.6.1694-1704.2004
Mutational analysis of the signal-sensing domain of ResE histidine kinase from Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
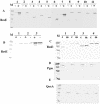
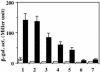
The Bacillus subtilis ResD-ResE two-component regulatory system activates genes involved in nitrate respiration in response to oxygen limitation or nitric oxide (NO). The sensor kinase ResE activates the response regulator ResD through phosphorylation, which then binds to the regulatory region of genes involved in anaerobiosis to activate their transcription. ResE is composed of an N-terminal signal input domain and a C-terminal catalytic domain. The N-terminal domain contains two transmembrane subdomains and a large extracytoplasmic loop. It also has a cytoplasmic PAS subdomain between the HAMP linker and C-terminal kinase domain. In an attempt to identify the signal-sensing subdomain of ResE, a series of deletions and amino acid substitutions were generated in the N-terminal domain. The results indicated that cytoplasmic ResE lacking the transmembrane segments and the extracytoplasmic loop retains the ability to sense oxygen limitation and NO, which leads to transcriptional activation of ResDE-dependent genes. This activity was eliminated by the deletion of the PAS subdomain, demonstrating that the PAS subdomain participates in signal reception. The study also raised the possibility that the extracytoplasmic region may serve as a second signal-sensing subdomain. This suggests that the extracytoplasmic region could contribute to amplification of ResE activity leading to the robust activation of genes required for anaerobic metabolism in B. subtilis.
Figures


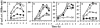
Similar articles
-
Involvement of ResE phosphatase activity in down-regulation of ResD-controlled genes in Bacillus subtilis during aerobic growth.J Bacteriol. 2001 Mar;183(6):1938-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.6.1938-1944.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11222591 Free PMC article.
-
Two-component regulatory proteins ResD-ResE are required for transcriptional activation of fnr upon oxygen limitation in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 1996 Jul;178(13):3796-802. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.13.3796-3802.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8682783 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of respiratory genes by ResD-ResE signal transduction system in Bacillus subtilis.Methods Enzymol. 2007;422:448-64. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)22023-8. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17628154
-
Anaerobic growth of a "strict aerobe" (Bacillus subtilis).Annu Rev Microbiol. 1998;52:165-90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.52.1.165. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9891797 Review.
-
Regulation of the anaerobic metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.Adv Microb Physiol. 2012;61:195-216. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394423-8.00005-6. Adv Microb Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23046954 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of DNA-binding specificity in the evolution of bacterial regulatory networks.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 6;379(3):627-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.008. Epub 2008 Apr 9. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18466918 Free PMC article.
-
The nitric oxide-responsive regulator NsrR controls ResDE-dependent gene expression.J Bacteriol. 2006 Aug;188(16):5878-87. doi: 10.1128/JB.00486-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16885456 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo characterization of the scaffold activity of flotillin on the membrane kinase KinC of Bacillus subtilis.Microbiology (Reading). 2015 Sep;161(9):1871-1887. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000137. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Microbiology (Reading). 2015. PMID: 26297017 Free PMC article.
-
ResDE Two-Component Regulatory System Mediates Oxygen Limitation-Induced Biofilm Formation by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Apr 2;84(8):e02744-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02744-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29427424 Free PMC article.
-
The Structure of the Periplasmic Sensor Domain of the Histidine Kinase CusS Shows Unusual Metal Ion Coordination at the Dimeric Interface.Biochemistry. 2016 Sep 20;55(37):5296-306. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00707. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27583660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavicchioli, R., R. C. Chiang, L. V. Kalman, and R. P. Gunsalus. 1996. Role of the periplasmic domain of the Escherichia coli NarX sensor-transmitter protein in nitrate-dependent signal transduction and gene regulation. Mol. Microbiol. 21:901-911. - PubMed
-
- Chamnongpol, S., M. Cromie, and E. A. Groisman. 2003. Mg2+ sensing by the Mg2+ sensor PhoQ of Salmonella enterica. J. Mol. Biol. 325:795-807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

