Cloning and sequence analysis of genes encoding Staphylococcus hyicus exfoliative toxin types A, B, C, and D
- PMID: 14996814
- PMCID: PMC355961
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.6.1833-1837.2004
Cloning and sequence analysis of genes encoding Staphylococcus hyicus exfoliative toxin types A, B, C, and D
Abstract
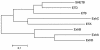
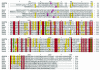
Exfoliative toxins produced by certain strains of Staphylococcus hyicus mediate exudative epidermitis in pigs. In this study the genes coding for four different exfoliative toxin from S. hyicus (ExhA, ExhB, ExhC, and ExhD) were cloned and sequenced. The coding sequence of the four toxin genes ranged from 816 to 834 bp. The amino acid sequences of these four toxins were homologous to the earlier described exfoliative toxins SHETB from S. hyicus and ETA, ETB, and ETD from Staphylococcus aureus. The homology between the S. hyicus toxins was at the same level as the homology to the exfoliative toxins from S. aureus. The toxins showed similarity to serine proteases, including preservation of the catalytic tract in ExhA, ExhB, and ExhC. However, in ExhD, Asp in the putative catalytic tract was replaced with Glu. The recombinant toxins could be expressed in Escherichia coli, and three of the four toxins were recognized by monoclonal antibodies raised against native exfoliative toxins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of genes encoding exfoliative toxins among Staphylococcus hyicus isolated in Russia and Germany.J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006 Nov;53(9):429-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2006.00988.x. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006. PMID: 17062120
-
Characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus hyicus from swine exudative epidermitis in South Korea.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Nov 28;20(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04396-y. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39609838 Free PMC article.
-
A multiplex PCR for detection of genes encoding exfoliative toxins from Staphylococcus hyicus.J Appl Microbiol. 2004;96(6):1265-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02258.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15139918
-
Staphylococcal exfoliative toxins: "molecular scissors" of bacteria that attack the cutaneous defense barrier in mammals.J Dermatol Sci. 2008 Jan;49(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.05.007. Epub 2007 Jun 19. J Dermatol Sci. 2008. PMID: 17582744 Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxins: how they cause disease.J Invest Dermatol. 2004 May;122(5):1070-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1747.2004.22144.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15140205 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A highly pathogenic strain of Staphylococcus sciuri caused fatal exudative epidermitis in piglets.PLoS One. 2007 Jan 10;2(1):e147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000147. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17215958 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence Analysis of Staphylococcus hyicus ATCC 11249T, an Etiological Agent of Exudative Epidermitis in Swine, Reveals a Type VII Secretion System Locus and a Novel 116-Kilobase Genomic Island Harboring Toxin-Encoding Genes.Genome Announc. 2015 Feb 19;3(1):e01525-14. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01525-14. Genome Announc. 2015. PMID: 25700402 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamyl Endopeptidases: The Puzzle of Substrate Specificity.Acta Naturae. 2017 Apr-Jun;9(2):17-33. Acta Naturae. 2017. PMID: 28740724 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of genes encoding staphylococcal enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, and exfoliative toxins in members of the Staphylococcus sciuri group.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Sep;43(9):4875-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4875-4876.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16145164 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus hyicus Isolates from Spanish Swine Farms.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Sep 11;13(9):871. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090871. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarestrup, F. M. 2001. Comparative ribotyping of Staphylococcus intermedius isolated from members of the Canoidea gives possible evidence for host-specificity and coevolution of bacteria and hosts. Int. J. Syst. E vol. Microbiol. 51:1343-13477. - PubMed
-
- Aarestrup, F. M., H. C. Wegener, and V. T. Rosdahl. 1995. Evaluation of phenotypic and genotypic methods for epidemiological typing of Streptococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis in Denmark. Vet. Microbiol. 45:139-150. - PubMed
-
- Amagai, M., N. Matsuyoshi, Z. H. Wang, C. Andl, and J. R. Stanley. 2000. Toxin in bullous impetigo and staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome targets desmoglein 1. Nat. Med. 6:1275-1277. - PubMed
-
- Amtsberg, G. 1979. Nachweis von Exfoliation auslösenden Substanzen in Kulturen von Staphylococcus hyicus des Schweines und Staphylococcus epidermidis Biotyp 2 des Rindes. Zentralbl. Vetmed. Reihe B 26:257-272. - PubMed
-
- Andresen, L. O. 1998. Differentiation and distribution of three types of exfoliative toxin produced by Staphylococcus hyicus from pigs with exudative epidermititis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 20:301-310. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

