Phase I study to determine the safety, tolerability and immunostimulatory activity of thalidomide analogue CC-5013 in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma and other advanced cancers
- PMID: 14997189
- PMCID: PMC2410215
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601579
Phase I study to determine the safety, tolerability and immunostimulatory activity of thalidomide analogue CC-5013 in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma and other advanced cancers
Abstract
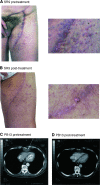
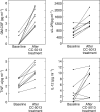
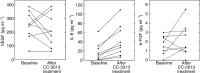
We assessed the safety, tolerability and efficacy of the immunomodulatory drug, CC-5013 (REVIMID trade mark ), in the treatment of patients with metastatic malignant melanoma and other advanced cancers. A total of 20 heavily pretreated patients received a dose-escalating regimen of oral CC-5013. Maximal tolerated dose, toxicity and clinical responses were evaluated and analysis of peripheral T-cell surface markers and serum for cytokines and proangiogenic factors were performed. CC-5013 was well tolerated. In all, 87% of adverse effects were classified as grade 1 or grade 2 according to Common Toxicity Criteria and there were no serious adverse events attributable to CC-5013 treatment. Six patients failed to complete the study, three because of disease progression, two withdrew consent and one was entered inappropriately and withdrawn from the study. The remaining 14 patients completed treatment without dose reduction, with one patient achieving partial remission. Evidence of T-cell activation was indicated by significantly increased serum levels of sIL-2 receptor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-12 (IL-12), tumour necrosis factor-alpha and IL-8 in nine patients from whom serum was available. However, levels of proangiogenic factors vascular endothelial growth factor and basic foetal growth factor were not consistently affected. This study demonstrates the safety, tolerability and suggests the clinical activity of CC-5013 in the treatment of refractory malignant melanoma. Furthermore, this is the first report demonstrating T-cell stimulatory activity of this class of compound in patients with advanced cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander LN, Wilcox CM (1997) A prospective trial of thalidomide for the treatment of HIV-associated idiopathic esophageal ulcers. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 13: 301–304 - PubMed
-
- Armitage JO (1998) Emerging applications of recombinant human granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood 92: 4491–4508 - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB (1997) The treatment of metastatic melanoma with chemotherapy and biologics. Curr Opin Oncol 9: 205–213 - PubMed
-
- Corral LG, Haslett PA, Muller GW, Chen R, Wong LM, Ocampo CJ, Patterson RT, Stirling DI, Kaplan G (1999) Differential cytokine modulation and T cell activation by two distinct classes of thalidomide analogues that are potent inhibitors of TNF-α. J Immunol 163: 380–386 - PubMed
-
- Davies FE, Raje N, Hideshima T, Lentzsch S, Young G, Tai YT, Lin B, Podar K, Gupta D, Chauhan D, Treon SP, Richardson PG, Schlossman RL, Morgan GJ, Muller GW, Stirling DI, Anderson KC (2001) Thalidomide and immunomodulatory derivatives augment natural killer cell cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Blood 98: 210–216 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

