ERK1/2 is activated in non-small-cell lung cancer and associated with advanced tumours
- PMID: 14997206
- PMCID: PMC2409626
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601644
ERK1/2 is activated in non-small-cell lung cancer and associated with advanced tumours
Abstract
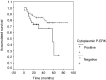
Activation of the ERK1/2 pathway is involved in malignant transformation both in vitro and in vivo. Little is known about the role of activated ERK1/2 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The purpose of this study was to characterise the extent of the activation of ERK1/2 by immunohistochemistry in patients with NSCLC, and to determine the relationship of ERK1/2 activation with clinicopathological variables. Specimens from 111 patients with NSCLC (stages I-IV) were stained for P-ERK. Staining for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Ki-67 was also performed. In all, 34% of the tumour specimens showed activation for ERK1/2, while normal lung epithelial tissue was consistently negative. There was a strong statistical correlation between nuclear and cytoplasmic P-ERK staining and advanced stages (P<0.05 and P<0.001, respectively), metastatic hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes (P<0.01, P<0.001), and higher T stages (P<0.01, P<0.001). We did not find correlation of nuclear or cytoplasmic P-ERK staining with either EGFR expression or Ki-67 expression. Total ERK1/2 expression was evaluated with a specific ERK1/2 antibody and showed that P-ERK staining was not due to ERK overexpression but rather to hyperactivation of ERK1/2. Patients with a positive P-ERK cytoplasmic staining had a significant lower survival (P<0.05). However, multivariate analysis did not show significant survival difference. Our study indicates that nuclear and cytoplasmic ERK1/2 activation positively correlates with stage, T and lymph node metastases, and thus, is associated with advanced and aggressive NSCLC tumours.
Figures

References
-
- Adeyinka A, Nui Y, Cherlet T, Snell L, Watson PH, Murphy LC (2002) Activated mitogen-activated protein kinase expression during human breast tumorigenesis and breast cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 8: 1747–1753 - PubMed
-
- Albanell J, Codony-Servat J, Rojo F, Del Campo JM, Sauleda S, Anido J, Raspall G, Giralt J, Rosello J, Nicholson RI, Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2001) Activated extracellular signal-regulated kinases: association with epidermal growth factor receptor/transforming growth factor alpha expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma and inhibition by anti-epidermal growth factor receptor treatments. Cancer Res 61: 6500–6510 - PubMed
-
- Albanell J, Rojo F, Averbuch S, Feyereislova A, Mascaro JM, Herbst R, LoRusso P, Rischin D, Sauleda S, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Baselga J (2002) Pharmacodynamic studies of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor ZD1839 in skin from cancer patients: histopathologic and molecular consequences of receptor inhibition. J Clin Oncol 20: 110–124 - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR (1995) PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 270: 27489–27494 - PubMed
-
- Allan LA, Morrice N, Brady S, Magee G, Pathak S, Clarke PR (2003) Inhibition of caspase-9 through phosphorylation at Thr 125 by ERK MAPK. Nat Cell Biol 7: 647–654 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

