Medical response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats
- PMID: 15001507
- PMCID: PMC381053
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.328.7439.568
Medical response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats
Abstract
Events that expose people to radiation are rare, but the threat of radiation injury is increasing. Doctors should know how to recognise and manage suspected exposure or contamination
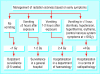
Figures



Comment in
-
Response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats: medical treatment should be given only when safe to do so.BMJ. 2004 May 1;328(7447):1074; author reply 1075. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7447.1074. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15117798 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats: other threats may be more serious.BMJ. 2004 May 1;328(7447):1074; author reply 1075. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7447.1074-a. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15117799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats: renunciation of nuclear weapons could lessen the threat.BMJ. 2004 May 1;328(7447):1074; author reply 1075. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7447.1074-b. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15117800 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats: other threats may be more serious.BMJ. 2004 May 1;328(7447):1074; author reply 1075. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7447.1074-a. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15117799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Contemporary management of radiation exposure and injury.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014 Sep;77(3):495-500. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000297. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014. PMID: 25159256 Review. No abstract available.
-
Emergency medical preparedness for radiological/nuclear incidents in the United States.J Radiol Prot. 2012 Mar;32(1):N27-32. doi: 10.1088/0952-4746/32/1/N27. Epub 2012 Mar 6. J Radiol Prot. 2012. PMID: 22395159
-
Medical management principles for radiation accidents.Mil Med. 2003 Mar;168(3):219-22. Mil Med. 2003. PMID: 12685687 Review.
-
Risks and management of radiation exposure.Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013 Sep;29(9):1016-26; quiz 1027-29. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182a380b8. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013. PMID: 24201986 Review.
Cited by
-
Infusion of Trx-1-overexpressing hucMSC prolongs the survival of acutely irradiated NOD/SCID mice by decreasing excessive inflammatory injury.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4;8(11):e78227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078227. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223778 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow and Peripheral Blood Cells Toxicity of a Single 2.0 Gy Cobalt60 Ionizing Radiation: An Animal Model.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2019 Mar;29(2):195-202. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v29i2.6. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2019. PMID: 31011267 Free PMC article.
-
Response to radiation incidents and radionuclear threats: medical treatment should be given only when safe to do so.BMJ. 2004 May 1;328(7447):1074; author reply 1075. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7447.1074. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15117798 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Establishing cytogenetic biodosimetry laboratory in Saudi Arabia and producing preliminary calibration curve of dicentric chromosomes as biomarker for medical dose estimation in response to radiation emergencies.3 Biotech. 2014 Dec;4(6):635-645. doi: 10.1007/s13205-014-0217-x. Epub 2014 Apr 18. 3 Biotech. 2014. PMID: 28324310 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological weapons: what type of threat?Crit Care. 2005 Jun;9(3):223-5. doi: 10.1186/cc3061. Epub 2005 Feb 17. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 15987404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Timins JK, Lipoti JA. Radiological terrorism. N J Med 2003;100: 14-21. - PubMed
-
- Yehezkelli Y, Dushnitsky T, Hourvitz A. Radiation terrorism: the medical challenge. Isr Med Assoc J 2002;4: 530-4. - PubMed
-
- Kilpatrick JJ. Nuclear attacks. RN. 2002;65: 46-51. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez AJ. Securing radioactive sources against terrorism: an international perspective. Health Phys Soc Newsl 2002;30: 3-5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
