The ABC transporter gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans has implications for the evolutionary dynamics of multidrug resistance in eukaryotes
- PMID: 15003118
- PMCID: PMC395765
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-3-r15
The ABC transporter gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans has implications for the evolutionary dynamics of multidrug resistance in eukaryotes
Abstract
Background: Many drugs of natural origin are hydrophobic and can pass through cell membranes. Hydrophobic molecules must be susceptible to active efflux systems if they are to be maintained at lower concentrations in cells than in their environment. Multi-drug resistance (MDR), often mediated by intrinsic membrane proteins that couple energy to drug efflux, provides this function. All eukaryotic genomes encode several gene families capable of encoding MDR functions, among which the ABC transporters are the largest. The number of candidate MDR genes means that study of the drug-resistance properties of an organism cannot be effectively carried out without taking a genomic perspective.
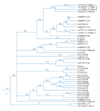
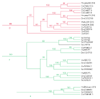
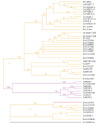
Results: We have annotated sequences for all 60 ABC transporters from the Caenorhabditis elegans genome, and performed a phylogenetic analysis of these along with the 49 human, 30 yeast, and 57 fly ABC transporters currently available in GenBank. Classification according to a unified nomenclature is presented. Comparison between genomes reveals much gene duplication and loss, and surprisingly little orthology among analogous genes. Proteins capable of conferring MDR are found in several distinct subfamilies and are likely to have arisen independently multiple times.
Conclusions: ABC transporter evolution fits a pattern expected from a process termed 'dynamic-coherence'. This is an unusual result for such a highly conserved gene family as this one, present in all domains of cellular life. Mechanistically, this may result from the broad substrate specificity of some ABC proteins, which both reduces selection against gene loss, and leads to the facile sorting of functions among paralogs following gene duplication.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Homologues of the human multidrug resistance genes MRP and MDR contribute to heavy metal resistance in the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.EMBO J. 1996 Nov 15;15(22):6132-43. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8947035 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo characterization of the drug resistance profile of the major ABC transporters and other components of the yeast pleiotropic drug resistance network.Microb Drug Resist. 1998 Fall;4(3):143-58. doi: 10.1089/mdr.1998.4.143. Microb Drug Resist. 1998. PMID: 9818966
-
The ABC transporter gene family of Daphnia pulex.BMC Genomics. 2009 Apr 21;10:170. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-170. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19383151 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug resistance: retrospect and prospects in anti-cancer drug treatment.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(16):1859-76. doi: 10.2174/092986706777585077. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842198 Review.
-
Mouse ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters Conferring Multi-Drug Resistance.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(4):423-32. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25929575 Review.
Cited by
-
A burst of ABC genes in the genome of the polyphagous spider mite Tetranychus urticae.BMC Genomics. 2013 May 10;14:317. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-317. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23663308 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters are required for efficient RNA interference in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Aug;17(8):3678-88. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-03-0192. Epub 2006 May 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16723499 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Brugia malayi ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in potentiating drug sensitivity.Parasitol Res. 2011 Nov;109(5):1311-22. doi: 10.1007/s00436-011-2378-4. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Parasitol Res. 2011. PMID: 21494842
-
Schistosome ABC multidrug transporters: From pharmacology to physiology.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2014 Sep 26;4(3):301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2014.09.007. eCollection 2014 Dec. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2014. PMID: 25516841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function of the Caenorhabditis elegans ABC transporter PGP-2 in the biogenesis of a lysosome-related fat storage organelle.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Mar;18(3):995-1008. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-08-0685. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17202409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Croop JM. Evolutionary relationships among ABC transporters. Methods Enzymol. 1998;292:101–116. - PubMed
-
- Higgins CF. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. - PubMed
-
- Childs S, Ling V. The MDR superfamily of genes and its biological implications. In: DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editor. In Important Advances in Oncology. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott; 1994. pp. 21–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

