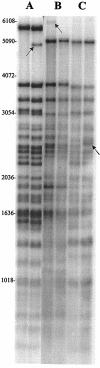
Stability of polymorphic GC-rich repeat sequence-containing regions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 15004103
- PMCID: PMC356821
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.3.1302-1304.2004
Stability of polymorphic GC-rich repeat sequence-containing regions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
Mycobacterium tuberculosis cultures were subjected to DNA fingerprinting with IS6110- and polymorphic GC-rich sequence (PGRS)-containing probes. The PGRS banding patterns remained highly stable during multiple cultures of specimens from one disease episode (0.5% changed) and during transmission in patients with close contact (1.9% changed). Characteristic PGRS-restriction fragment length polymorphism motifs for different strain groupings may indicate distant evolutionary events leading to the differentiation of M. tuberculosis strain lineages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of restriction fragment length polymorphism with the polymorphic guanine-cytosine-rich sequence and spoligotyping for differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates with five or fewer copies of IS6110.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Feb;48(2):575-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01604-09. Epub 2009 Dec 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20032250 Free PMC article.
-
IS6110 transposition and evolutionary scenario of the direct repeat locus in a group of closely related Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains.J Bacteriol. 1998 Apr;180(8):2102-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.8.2102-2109.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9555892 Free PMC article.
-
Spoligotyping and polymorphic GC-rich repetitive sequence fingerprinting of mycobacterium tuberculosis strains having few copies of IS6110.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Oct;38(10):3572-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.10.3572-3576.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11015365 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IS6110 in the evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007 Sep;87(5):393-404. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2007.05.010. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2007. PMID: 17627889 Review.
-
Genetic markers for the epidemiology of tuberculosis.Res Microbiol. 1992 May;143(4):385-91. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90051-o. Res Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1360692 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Comparison of restriction fragment length polymorphism with the polymorphic guanine-cytosine-rich sequence and spoligotyping for differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates with five or fewer copies of IS6110.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Feb;48(2):575-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01604-09. Epub 2009 Dec 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20032250 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro analysis of rates and spectra of mutations in a polymorphic region of the Rv0746 PE_PGRS gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Bacteriol. 2007 Mar;189(5):2190-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.01647-06. Epub 2006 Dec 15. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17172340 Free PMC article.
-
Genotyping of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: application in epidemiologic studies.Future Microbiol. 2011 Feb;6(2):203-16. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.165. Future Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21366420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cole, S. T., R. Brosch, J. Parkhill, T. Garnier, C. Churcher, D. Harris, S. V. Gordon, K. Eiglmeier, S. Gas, C. E. Barry III, F. Tekaia, K. Badkock, D. Basham, D. Brown, T. Chillingworth, R. Connor, R. Davies, K. Devlin, T. Feltwell, S. Gentles, N. Hamlin, S. Holroyd, T. Hornsby, K. Jagels, A. Krogh, J. McLean, S. Moule, L. Murphy, K. Olivier, J. Osborne, M. A. Quail, M.-A. Rajandream, J. Rogers, S. Rutter, K. Seeger, J. Skelton, R. Squares, S. Squares, J. E. Sulston, K. Taylor, S. Whitehead, and B. G. Barrell. 1998. Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 393:537-544. - PubMed
-
- De Boer, A. S., M. W. Borgdorff, P. E. de Haas, N. J. Nagelkerke, J. D. van Embden, and D. van Soolingen. 1999. Analysis of rate of change of IS6110 RFLP patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on serial patient isolates. J. Infect. Dis. 180:1238-1244. - PubMed
-
- Kamerbeek, J., L. Schouls, A. Kolk, M. van Agterveld, D. van Soolingen, S. Kuijper, A. Bunschoten, H. Molhuizen, R. Shaw, M. Goyal, and J. van Embden. 1997. Simultaneous detection and strain differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for diagnosis and epidemiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:907-914. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous