First isolation of Borrelia lusitaniae from a human patient
- PMID: 15004107
- PMCID: PMC356816
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.3.1316-1318.2004
First isolation of Borrelia lusitaniae from a human patient
Abstract
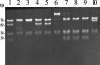
The first human isolate of Borrelia lusitaniae recovered from a Portuguese patient with suspected Lyme borreliosis is described. This isolate, from a chronic skin lesion, is also the first human isolate of Borrelia in Portugal. Different phenotypic and molecular methods are used to characterize it.
Figures


References
-
- Baptista, S., A. Quaresma, T. Aires, K. Kurtenbach, M. Santos-Reis, M. Nicholson, and M. Collares-Pereira. Lyme borreliosis spirochetes in questing ticks from mainland Portugal. Int. J. Med. Microbiol., in press. - PubMed
-
- Collares-Pereira, M., S. C. Santos, and M. L. Vieira. 2000. Valor diagnóstico da técnica de imunofluorescência indirecta utilizando diferentes preparações antigénicas no imunodiagnóstico da Borreliose de Lyme em Portugal. Supl. Trab. Soc. Port. Dermatol. Venereol. 58:97-105.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

