Modulation of arterial baroreflex dynamic response during mild orthostatic stress in humans
- PMID: 15004207
- PMCID: PMC1665045
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.057133
Modulation of arterial baroreflex dynamic response during mild orthostatic stress in humans
Abstract
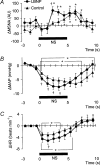
We tested the hypothesis that in humans, carotid-baroreflex dynamic responses (evaluated by examining the time course of the carotid-baroreflex-induced alterations in muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR)) would be altered during mild orthostatic stress in ways that serve to limit orthostatic hypotension. In 12 healthy subjects (10 male, 2 female), 5-s periods of neck pressure (NP) (50 mmHg) and neck suction (NS) (-60 mmHg) were used to evaluate carotid baroreflex function at rest (CON) and during lower body negative pressure (LBNP) (-15 mmHg). During LBNP (as compared with CON) (a) the augmentations in MSNA and MAP elicited by NP were greater, (b) the NS-induced period of MSNA suppression was, if anything, shorter, (c) the peak decrement in MAP elicited by NS, although not different in amplitude, occurred earlier and recovered to its initial level more quickly after NS, and (d) the HR responses to NP and NS were greater. These results suggest that during mild orthostatic stress, carotid-baroreflex dynamic responses are modulated in ways that should help maintain blood pressure and limit orthostatic hypotension.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of arterial baroreflex dynamic response during muscle metaboreflex activation in humans.J Physiol. 2002 Nov 1;544(3):939-48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.024794. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12411536 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity during severe orthostatic stress.J Physiol. 2006 Nov 1;576(Pt 3):947-58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.117507. Epub 2006 Aug 17. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16916904 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of unilateral and bilateral carotid baroreflex stimulation on cardiac and neural sympathetic discharge oscillatory patterns.Circulation. 2003 Aug 12;108(6):717-23. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000084540.91605.0C. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 12900347 Clinical Trial.
-
Sympathetic nerve activity in hypotension and orthostatic intolerance.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Mar;177(3):359-65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2003.01081.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12609007 Review.
-
Vestibular activation of sympathetic nerve activity.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Mar;177(3):313-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2003.01084.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 12609001 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Skeletal Muscle Pump During Lower Limb Counterpressure: Lags and Causality in Cardiovascular Regulation.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Aug;16(4):e70019. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.70019. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025. PMID: 40741773 Free PMC article.
-
Heat stress enhances arterial baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity via increased sensitivity of burst gating, not burst area, in humans.J Physiol. 2006 Jun 1;573(Pt 2):445-51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108662. Epub 2006 Mar 31. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16581857 Free PMC article.
-
Combined influence of inspiratory loading and locomotor subsystolic cuff inflation on cardiovascular responses during submaximal exercise.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020 May 1;128(5):1338-1345. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00781.2019. Epub 2020 Apr 2. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020. PMID: 32240016 Free PMC article.
-
Sex comparisons in muscle sympathetic nerve activity and arterial pressure oscillations during progressive central hypovolemia.Physiol Rep. 2015 Jun;3(6):e12420. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12420. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26109186 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle sympathetic nerve activity during exercise.J Physiol Sci. 2019 Jul;69(4):589-598. doi: 10.1007/s12576-019-00669-6. Epub 2019 May 3. J Physiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31054082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bevegård S, Castenfors J, Lindblad E, Tranesjö J. Blood pressure and heart rate regulation capacity of the carotid sinus during changes in blood volume distribution in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977;99:300–312. - PubMed
-
- Delius W, Hagbarth KE, Hongell A, Wallin BG. General characteristics of sympathetic activity in human muscle nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972;84:65–81. - PubMed
-
- Eckberg DL. Nonlinearities of the human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex. Circ Res. 1980;47:208–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

