Cyclase-associated protein 1 (CAP1) promotes cofilin-induced actin dynamics in mammalian nonmuscle cells
- PMID: 15004221
- PMCID: PMC404026
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-01-0048
Cyclase-associated protein 1 (CAP1) promotes cofilin-induced actin dynamics in mammalian nonmuscle cells
Abstract
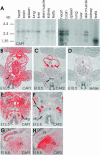
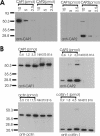
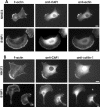
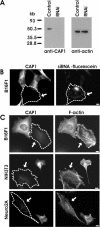
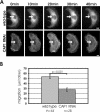
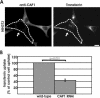
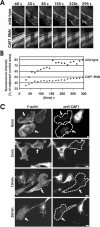
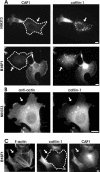
Cyclase-associated proteins (CAPs) are highly conserved actin monomer binding proteins present in all eukaryotes. However, the mechanism by which CAPs contribute to actin dynamics has been elusive. In mammals, the situation is further complicated by the presence of two CAP isoforms whose differences have not been characterized. Here, we show that CAP1 is widely expressed in mouse nonmuscle cells, whereas CAP2 is the predominant isoform in developing striated muscles. In cultured NIH3T3 and B16F1 cells, CAP1 is a highly abundant protein that colocalizes with cofilin-1 to dynamic regions of the cortical actin cytoskeleton. Analysis of CAP1 knockdown cells demonstrated that this protein promotes rapid actin filament depolymerization and is important for cell morphology, migration, and endocytosis. Interestingly, depletion of CAP1 leads to an accumulation of cofilin-1 into abnormal cytoplasmic aggregates and to similar cytoskeletal defects to those seen in cofilin-1 knockdown cells, demonstrating that CAP1 is required for proper subcellular localization and function of ADF/cofilin. Together, these data provide the first direct in vivo evidence that CAP promotes rapid actin dynamics in conjunction with ADF/cofilin and is required for several central cellular processes in mammals.
Figures
References
-
- Arber, S., Barbayannis, F.A., Hanser, H., Schneider, C., Stanyon, C.A., Bernard, O., and Caroni, P. (1998). Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature 393, 805–809. - PubMed
-
- Ayscough, K.R., Stryker, J., Pokala, N., Sanders, M., Crews, P., and Drubin, D.G. (1997). High rates of actin filament turnover in budding yeast and roles for actin in establishment and maintenance of cell polarity revealed using the actin inhibitor latrunculin-A. J. Cell Biol. 137, 399–416. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balcer, H.I., Goodman, A.L., Rodal, A.A., Smith, E., Kugler, J., Heuser, J.E., and Goode, B.L. (2003). Coordinated regulation of actin filament turnover by a high molecular weight Srv2/CAP complex, cofilin, profilin, and Aip1. Curr. Biol. 13, 2159–2169. - PubMed
-
- Ballestrem, C., Wehrle-Haller, B., and Imhof, B.A. (1998). Actin dynamics in living mammalian cells. J. Cell Sci. 111, 1649–1658. - PubMed
-
- Baum, B., Li, W., and Perrimon, N. (2000). A cyclase-associated protein regulates actin and cell polarity during Drosophila oogenesis and in yeast. Curr. Biol. 10, 964–973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

