Uncoated endocytic vesicles require the unconventional myosin, Myo6, for rapid transport through actin barriers
- PMID: 15004223
- PMCID: PMC404020
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-01-0002
Uncoated endocytic vesicles require the unconventional myosin, Myo6, for rapid transport through actin barriers
Abstract
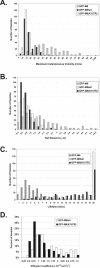
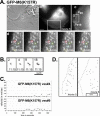
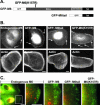
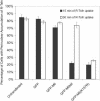
After clathrin-mediated endocytosis, clathrin removal yields an uncoated vesicle population primed for fusion with the early endosome. Here we present the first characterization of uncoated vesicles and show that myo6, an unconventional myosin, functions to move these vesicles out of actin-rich regions found in epithelial cells. Time-lapse microscopy revealed that myo6-associated uncoated vesicles were motile and exhibited fusion and stretching events before endosome delivery, processes that were dependent on myo6 motor activity. In the absence of myo6 motor activity, uncoated vesicles remained trapped in the actin mesh, where they exhibited Brownian-like motion. Exit from the actin mesh occurred by a slow diffusion-based mechanism, delaying transferrin trafficking to the early endosome. Expression of a myo6 mutant that bound tightly to F-actin produced immobilized vesicles and blocked trafficking. Depolymerization of the actin cytoskeleton rescued this block and specifically accelerated transferrin delivery to the early endosome without affecting earlier steps in endocytosis. Therefore actin is a physical barrier impeding uncoated vesicle trafficking, and myo6 is recruited to move the vesicles through this barrier for fusion with the early endosome.
Figures


References
-
- Bose, A., Guilherme, A., Robida, S.I., Nicoloro, S.M.C., Zhou, Q.L., Jiang, Z.Y., Pomerleau, D.P., and Czech, M.P. (2002). Glucose transporter recycling in response to insulin is facilitated by mysoin Myo1c. Nature 420, 821–824. - PubMed
-
- Cramer, L.P. (1997). Molecular mechanism of actin-dependent retrograde flow in lamellipodia of motile cells. Front. Biosci. 2, d260–d270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

