Dynamic regulation of a GPCR-tetraspanin-G protein complex on intact cells: central role of CD81 in facilitating GPR56-Galpha q/11 association
- PMID: 15004227
- PMCID: PMC404030
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-12-0886
Dynamic regulation of a GPCR-tetraspanin-G protein complex on intact cells: central role of CD81 in facilitating GPR56-Galpha q/11 association
Abstract
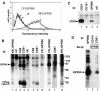
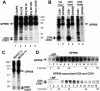
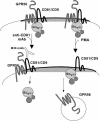
By means of a variety of intracellular scaffolding proteins, a vast number of heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) may achieve specificity in signaling through a much smaller number of heterotrimeric G proteins. Members of the tetraspanin family organize extensive complexes of cell surface proteins and thus have the potential to act as GPCR scaffolds; however, tetraspanin-GPCR complexes had not previously been described. We now show that a GPCR, GPR56/TM7XN1, and heterotrimeric G protein subunits, Galpha(q), Galpha(11), and Gbeta, associate specifically with tetraspanins and CD81, but not with other tetraspanins. CD9 Complexes of GPR56 with CD9 and CD81 remained intact when fully solubilized and were resistant to cholesterol depletion. Hence they do not depend on detergent-insoluble, raft-like membrane microdomains for stability. A central role for CD81 in promoting or stabilizing a GPR56-CD81-Galpha(q/11) complex was revealed by CD81 immunodepletion and reexpression experiments. Finally, antibody engagement of cell surface CD81 or cell activation with phorbol ester revealed two distinct mechanisms by which GPR56-CD81-Galpha(q/11) complexes can be dynamically regulated. These data reveal a potential role for tetraspanins CD9 and CD81 as GPCR scaffolding proteins.
Figures





Similar articles
-
FPRP, a major, highly stoichiometric, highly specific CD81- and CD9-associated protein.J Biol Chem. 2001 Feb 16;276(7):4853-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009859200. Epub 2000 Nov 21. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11087758
-
Phosphatidic acid regulates signal output by G protein coupled receptors through direct interaction with phospholipase C-beta(1).Cell Signal. 2009 Sep;21(9):1379-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.04.005. Epub 2009 May 3. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19414067
-
Signaling through a G Protein-coupled receptor and its corresponding G protein follows a stoichiometrically limited model.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 29;282(26):19203-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701558200. Epub 2007 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17420253
-
Signaling through G protein coupled receptors.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Oct;4(10):942-7. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.10.9530. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19826234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strike a pose: Gαq complexes at the membrane.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Jan;35(1):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.10.008. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24287282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): biological functions and potential drug targets.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Mar;33(3):363-71. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.210. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22367282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of G protein-coupled receptor 56 is associated with tumor progression in non-small-cell lung carcinoma patients.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Jul 5;9:4105-12. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S106907. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27462165 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD9 in proliferation and proangiogenic action of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Nov;455(2):283-96. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0285-4. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17668233
-
The orphan adhesion G protein-coupled receptor GPR97 regulates migration of lymphatic endothelial cells via the small GTPases RhoA and Cdc42.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 13;288(50):35736-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.512954. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24178298 Free PMC article.
-
GPR56 function as a key repressor in hepatocyte pyroptosis and the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 6;23(1):632. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06619-8. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40481471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berditchevski, F. (2001). Complexes of tetraspanins with integrins: more than meets the eye. J. Cell Sci. 114, 4143–4151. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., Bazzoni, G., and Hemler, M.E. (1995). Specific association of CD63 with the VLA-3 and VLA-6 integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 17784–17790. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., Chang, S., Bodorova, J., and Hemler, M.E. (1997a). Generation of monoclonal antibodies to integrin-associated proteins. Evidence that alpha3beta1 complexes with EMMPRIN/basigin/OX47/M6. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 29174–29180. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., Tolias, K.F., Wong, K., Carpenter, C.L., and Hemler, M.E. (1997b). A novel link between integrins, transmembrane-4 superfamily proteins (CD63 and CD81), and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 2595–2598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

